Endoscopic Management of BPH
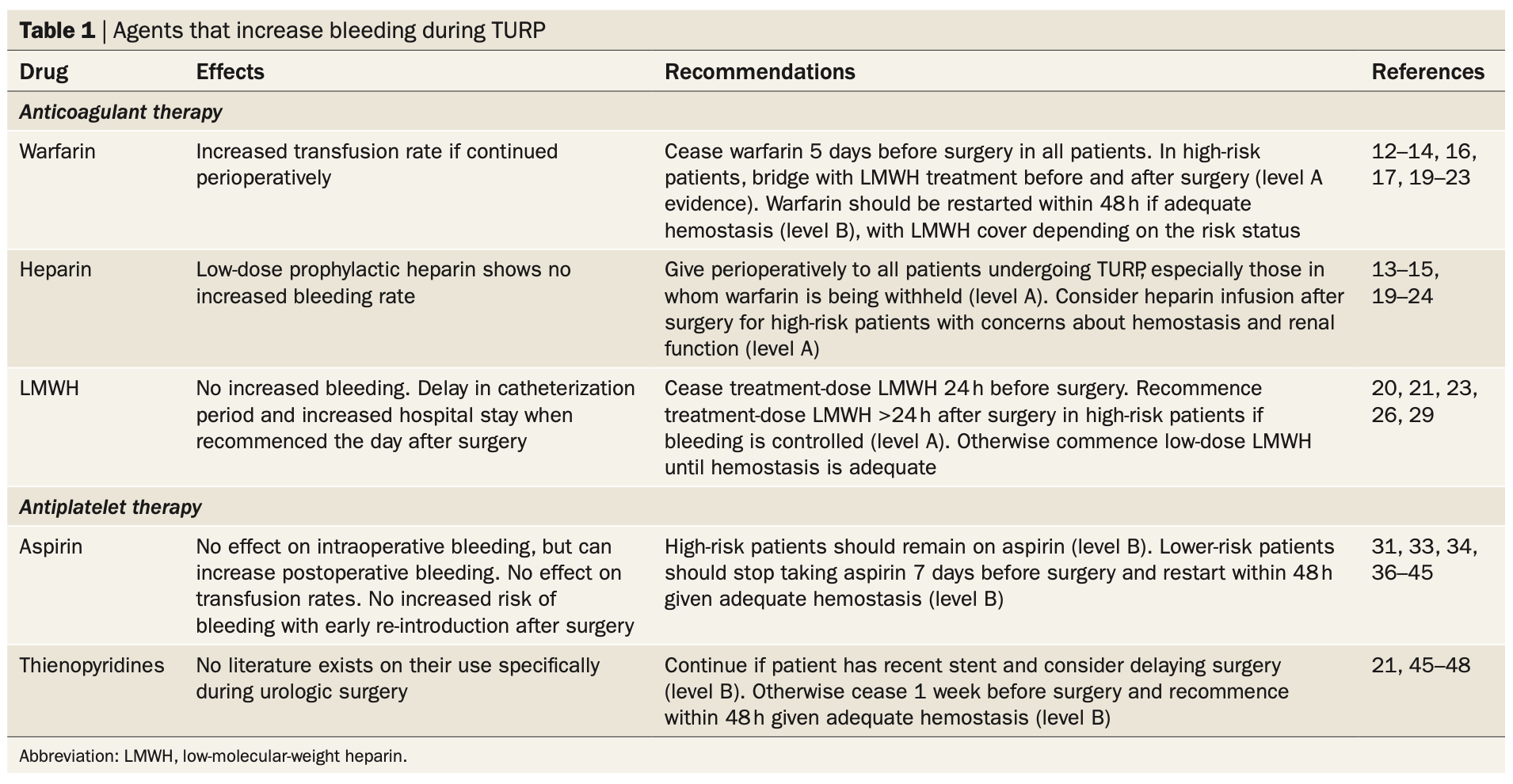
Anticoagulation plans prior to TURP, from Kavanagh 2011
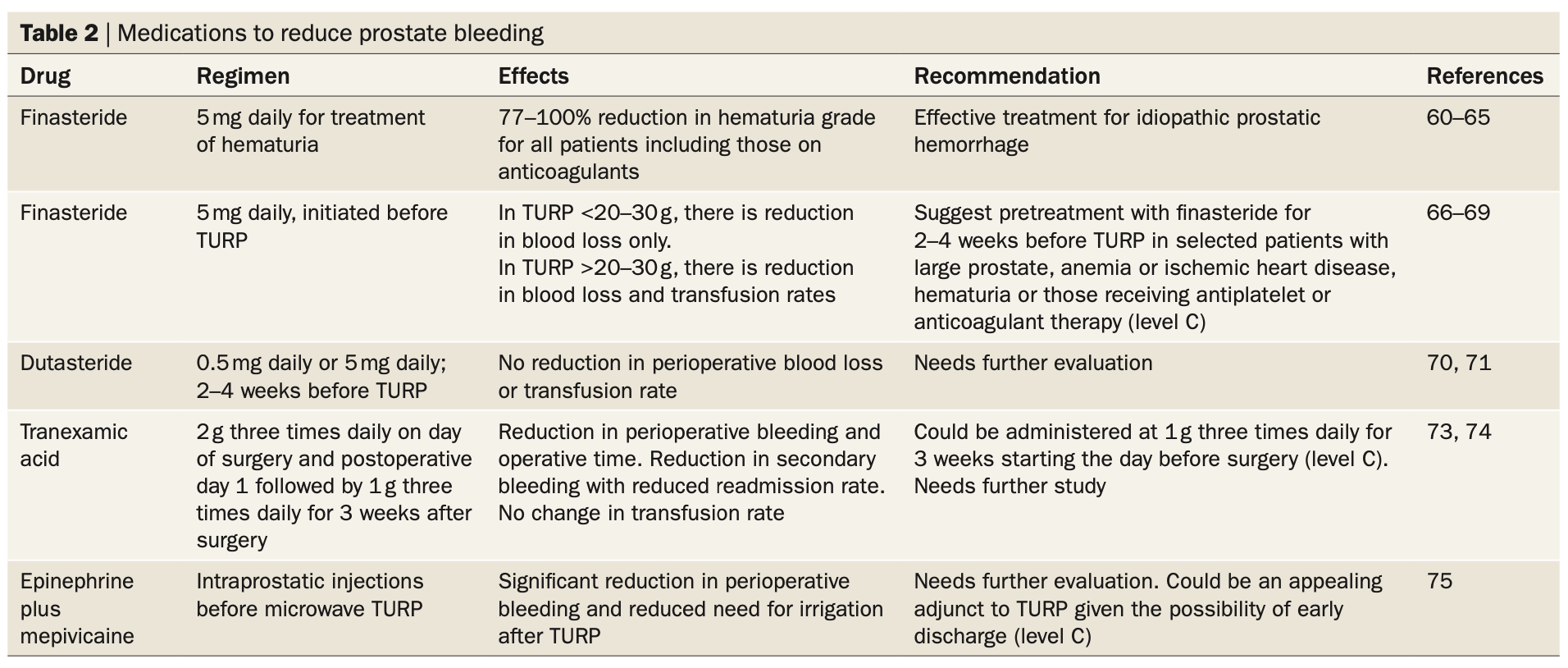
Medications that decrease bleeding during TURP, from Kavanagh 2011
Transurethral resection of prostate (TURP)
Preoperative considerations
- Anticoagulation: higher risk for postoperative transfusion, clot retention, and VTE, consider laser prostatectomy
- Counsel that retrograde ejaculation occurs in 62-78%
- Erections: 30% report improvement vs 20% report worsening, overall no change in sexual activity
Operative technique
- Dorsal lithotomy, genitals at edge of bed, optimize space between legs by spreading knees
- Resectoscope: 30 degree lens, yellow sheath (26Fr), visual obturator
- Confirm bi vs mono polar equipment and irrigation
- Prep and drape patient
- Set up light + camera cord and irrigation fluid with stopcock
- Place sound in meatus to passively dilate urethra
- Lubricate entire scope length (minimizes stricture formation)
- Insert resectoscope, empty bladder, examine prostate, verumontanum, and ureteral orifices
- Resect prostate starting with median lobe, then move anteriorly for lateral lobes
- Reassess and repeat resection for adenoma as needed, shorter swipes near apex
- Obtain hemostasis as needed
- Remove chips with Ellik or Toomey syringe
- Repeat obtaining hemostasis, reassess at lower pressure
- Remove scope with bladder full (may see passive drainage), place 20Fr 3-way catheter and inflate with 30mL sterile water, irrigate to confirm placement and drainage
Operative Tips
- Bipolar vs monopolar: bipolar has no risk TUR syndrome but monopolar better at hemostasis, mainly surgeon preference
- Anesthesia: can consider spinal if high risk
- Bipolar settings: 200 resection, 120 vaporization
- Monopolar settings: 90 cut, 60 coag
- Chip length: avoid short chips, prolongs resection time and makes identifying bleeding more difficult
- Visualization: always keep 1/4 loop visible to maintain same resection depth
- Fulcrum: sweep hands in opposite direction of resection (think clock face), allows loop to resect entire depth of prostate (shaped like a bowl)
- Collecting chips: cut off top and bottom of suction bag to isolate chips then scoop directly into specimen cup
- TUR syndrome: more common in larger glands (> 45g) and longer surgeries (> 90min)
- Intraoperative erection: rare, may require phenylephrine injection
Expected postoperative course
- Void trial POD#1
- If patient passes, discharge POD#1 without catheter
- If patient fails, replace catheter, void trial in 3-5 days
- Stool softeners to prevent constipation (can cause hematuria from straining)
- Avoid physical activity causing perineal pressure for 4-6 weeks
- Intermittent hematuria and dysuria normal for 4-6 weeks
- 75-93% report improved voiding symptoms
Postoperative complication management
- Bleeding: fill balloon to 50-60mL, place catheter on traction, transfuse prn
- Bladder neck contracture: 2%, slowly decreasing flow rates, confirm with cystoscopy, open laterally until it accommodates cystoscope, can give methylene blue to identify obliterated opening
- Stricture: 4%, lubricate scope to prevent intraop, low rates with SP catheters over urethral catheters
Prostatic Urethral Lift (UroLift)
Preoperative considerations
- Contraindicated if history urinary retention
- Perform cystoscopy to rule out presence of median lobe
- Perform sizing, less effective for glands > 80g
- Should have minimal effect on erectile and ejaculatory function (no tissue removed)
Operative technique
- Place patient in dorsal lithotomy position, prep/drape similar to TURP
- Insert cystoscope, inspect bladder and prostate
- Position device 1.5cm distal to bladder neck, visualizing verumontanum
- Unlock safety
- Compress against prostatic tissue at 2 or 10 oclock (anterolateral position)
- Pull needle trigger (blue trigger)
- Pull retraction trigger (gray trigger) to pull needle back
- Move scope proximally towards bladder until silver line visible
- Push urethral release button to cut suture
- Usually place 4 implants, more if needed
Postoperative management
- 1/3 failed immediate void trial and required catheter for ~1 day
- Up to 2% have inadequately placed implants and need removal due to encrustation
- Many patients will likely require a second treatment in the future due to tissue growth
Photovaporization (PVP, KTP)
Preoperative considerations
- Useful for patients on active anticoagulation, but best if patients can be bridged
- Works best for prostates < 80-100g
Operative technique
- Position similar to TURP (see above), prep/drape
- Set up separate laser irrigation cord, keep closed until ready to start surgery (will avoid running out of fluid
- Reverse trendelenberg to 6 degrees (forces bubbles into bladder to improve visualization)
- Dilate meatus and lubricate entire scope length
- Insert cystoscope into bladder, assess location of ureters and trigone relative to bladder neck
- After inspecting, open laser and attach to irrigation fluid
- Position laser so blue triangle is visible (can damage scope if laser too close)
- Can rapidly zap entire prostate on 80 to superficially cauterize all tissue
- Take down median lobe, either by creating lateral channels first or just working from one side to the other
- Increase the energy level as needed (120+)
- Maintain appropriate distance and timing, otherwise laser with coagulate and not vaporize
- Obtain hemostasis as needed
- Can consider giving 20mg IV furosemide to assist with diuresis
- Place 18Fr 2-way or 22Fr 3-way (if concerned for bleeding
- Disposition: admit and perform void trial in AM, admit and discharge with catheter in AM for clinic void trial, or discharge from PACU with catheter for clinic void trial
Postoperative management
- Maintain fluid intake to minimize hematuria
- Dysuria minimized by avoiding accidental tissue coagulation during surgery, can treat with NSAIDs and occasionally a steroid taper
- Transfusion need is rare
Transurethral Incision of Prostate (TUIP)
Preoperative considerations
- Useful for younger patients who want to avoid retrograde ejaculation
- Size: best candidates are small glands (< 30g)
- Median lobe is not a contraindication
Operative technique
- Position similar to above
- Insert resectoscope and examine prostate and bladder neck
- Incise at 5 o'clock or 7 o'clock positions, unilaterally or bilaterally
- Can incise with laser or hot knife
- Incise down to surgical capsule (some incise down to periprostatic fat)
- Obtain hemostasis
- Insert catheter to monitor immediate urine appearance
Postoperative management
- Can keep overnight or discharge immediately, with(out) catheter
- Retrograde ejaculation: 0-37%, less with unilateral incision
Reported Surgical Complications (from Campbell's)
| mTURP | bTURP | TUNA | TUMT | HoLEP | PVP | TUVP | TUIP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporary retention | 4.3-6.8% | 3.3-3.7% | 23% | 10-24% | 2.7-5.9% | 5.2-9.9% | 2-9.8% | 4.9-11.3% |
| UTI | 4.1-6.2% | 2.6-8.4% | 4% | 15-20% | 0.9-2.7% | 4.2-12% | 0% | - |
| BNC | 2-3.2% | 0.5% | - | 0% | 1.2-1.5% | 1.1-5% | 0.5-1% | - |
| Stricture | 3.4-4.1% | 0.5-4.7% | 0.5% | 0-2% | 1.9-4.4% | 1-6.3% | 1.9-3.3% | 2.9-8.8% |
| Incontinence | 0.6-1.5% | 0-1% | - | - | 0.9-1.1% | 0-0.4% | 0-2% | 0.3-1.8% |
| Transfusion | 2-4.4% | 1.5-2.3% | rare | 0% | 0-1% | 0% | 0-0.5% | 1.1% |
| Clot retention | 4.9-7.2% | 2.7-7.9% | - | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0-0.5% | - |
| Hematuria | 3.5-15.7% | 1% | 6-28% | 1-26% | 0% | 0.7% | 0% | 4.3% |
| Dysuria | 0.8% | 0% | 8-14% | 14% | 1.2% | 8.5-13.9% | 2.9% | - |
| Urgency | 2.2% | 0.2% | 10% | - | 5.6% | 0% | 0% | - |
| Storage symptoms | - | - | - | 18-31% | - | - | 21% | - |
| Reoperation for BPE | 0.5% | 0.2% | 19% | 4% | 0% | 0.7-5.6% | 2.4% | - |
| Reoperation other than for BPE | 1.1% | 0.2% | 0% | - | 1.9-2.8% | - | 5.4% | 9.6-18.4% |
| Capsular perforation | 0.1% | 0% | - | - | 0.2% | 0% | 0% | - |
| Conversion to TURP | n/a | 0% | n/a | n/a | 0% | 3.5% | 0% | - |
| TUR syndrome | 0.8-2.5% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | - |
| Bladder mucosal injury | 0% | 0% | 0% | - | 3.3% | 0% | 0% | - |
References
- Helo, S., C. Welliver, and K. McVary. "Minimally Invasive and Endoscope Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Kavanagh, Liam E., Gregory S. Jack, and Nathan Lawrentschuk. "Prevention and management of TURP-related hemorrhage." Nature Reviews Urology 8.9 (2011): 504-514.