Disorders of Male Ejaculation
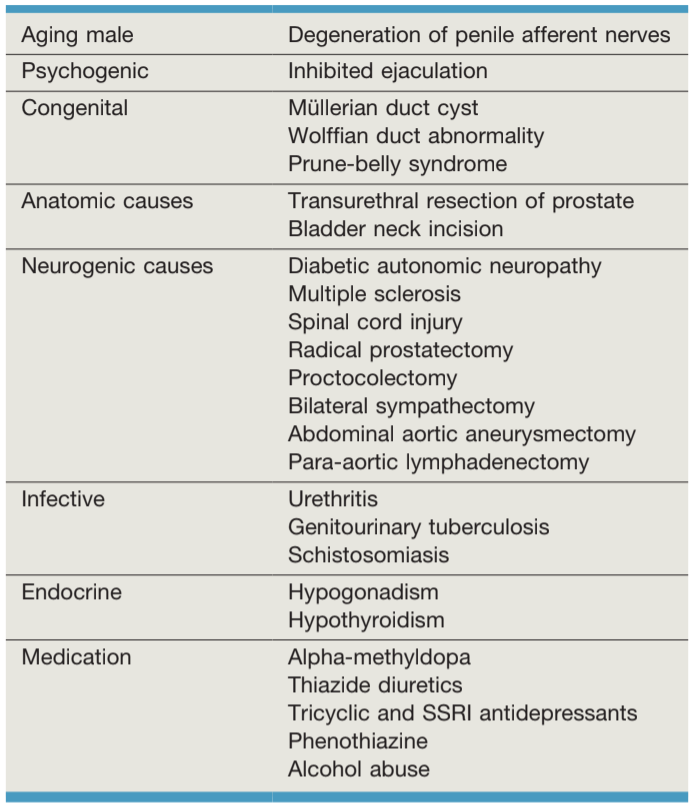
Causes of delayed ejaculation, from Campbell's

Questions to assess delayed ejaculation, from Campbell's
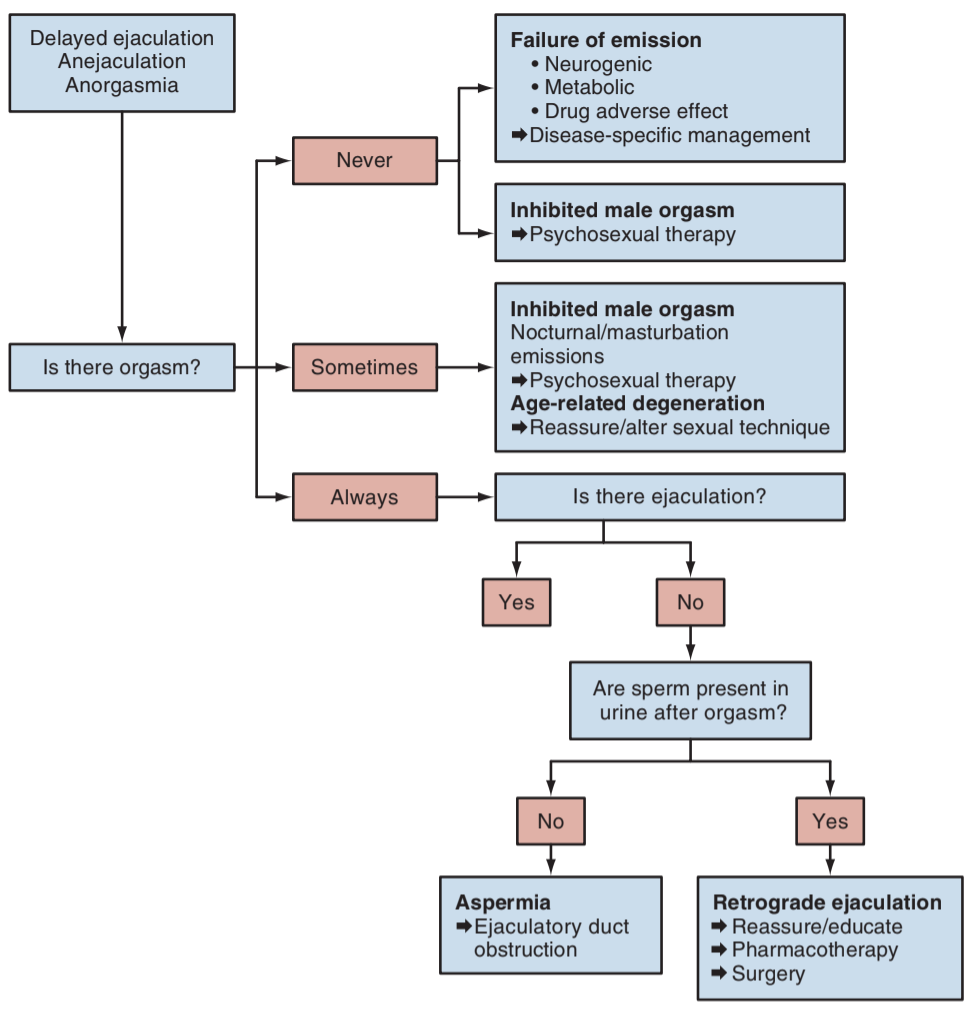
Algorithm for managing delayed ejaculation, from Campbell's
Delayed ejaculation
- Definition: any disorder resulting in delayed/absent ejaculation 75-100% of sexual interactions
- Most common causes: psychogenic, aging, hypogonadism, hypothyroid, diabetes, SSRI, prior prostate/pelvic surgery, prior radiation
- Cutaneous nerve testing: assess sensory function of the penis, may indicate sensory neuropathy
- Labs: recommended to check testosterone levels, consider evaluating DM or hypothyroid
- Management: switch SSRIs or other meds, psychosexual therapy (helpful to include partner in discussion), consider vibratory stimulation, altering sexual practices
- Medications: options include cabergoline, pramiprexole, amantadine, bupropion, pseudoephedrine, reboxetine, buspirone, cyproheptadine, oxytoxcin, but have limited evidence and are indicated for patient-specific situations
Painful ejaculation
- Location: may be penile, scrotal, perineal
- Causes: infection, stricture, prior vasectomy, prior hernia repair, ejaculatory duct obstruction, seminal vesicle calculi, prior XRT
- Exam: assess location of pain, perform DRE (check for BPH/cancer and pelvic floor dysfunction)
- Pelvic pain during orgasm + anejaculation: may indicate ejaculatory duct obstruction
- Pelvic floor dysfunction: patients may also report pain with urination and bowel movements in addition to sexually-related pain
- Treatment: depends on underlying cause, a-blockers may actually increase pain
Hematospermia
- Causes: infection, stones, prior trauma, constipation, obstruction, cysts, cancer, vascular abnormalities, recent GU instrumentation/surgery
- Malignancy risk: 1.4% if < 40yo, 6.2% if > 40yo, cause is almost always benign
- Evaluation: risk factors, GU exam, DRE, urinalysis, may require STI and Tb testing, consider PSA testing if > 40yo
- Adjunct testing: consider TRUS, semen culture, cystoscopy, pelvic MRI
- Management: often self-limiting, can aspirate or unroof cysts, consider embolization/excision if severe uncontrolled bleeding
Other male sexual dysfunctions
- Ejaculatory anhedonia: minimal pleasure with ejaculation/orgasm, check hormone levels and history, consider psychotherapy or treatment of hormonal causes
- Post-SSRI sexual dysfunction: reported 5-15%, may persist for months/years and spontaneously resolve
- Postorgasmic illness syndrome: rare, may be due to hypersensitivity reaction with their own semen
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- McMahon, C. "Disorders of Male Orgasm and Ejaculation." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Shindel, Alan W., et al. "Disorders of ejaculation: an AUA/SMSNA guideline." (2020).
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.