Male Infertility
Workup
Normal sperm development
- Spermatogenesis: occurs in spermatic tubules, mitosis (spermatogonia to spermatocytes), meiosis x2 (primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes to spermatids), spermiogenesis (spermatids to spermatozoa)
- Maturation: occurs in epididymis, acquire mobility and capacity to fertilize, completed at epididymal tail (stored here)
- Capacitation: activation of sperm's ability to fertilize egg, only occurs in female genital tract
- Hypermobility: increased mobility occurs after capacitation (only in female genital tract)
- Acrosome reaction: head of sperm releases enzymes to dissolve the outer layer of ovum
Normal male ejaculation
- Controlled by spinal ejaculatory center (T12-L2)
- Emission: sympathetic mediated, bladder neck contraction, release of fluid into posterior urethra (stimulates urethral-muscle reflex)
- Expulsion: activated by urethral-muscle reflex, contraction of bulbospongiosus/ischiocavernosus, mediated by pudendal nerve
Timing the workup
- Wait 1yr before starting workup, 6mo if woman > 35yo
- 75% can achieve pregnancy within 6mo trying, 85% within 12mo, 90% within 2yr
- 30% male infertility will be identified as idiopathic
- Both partners need to undergo workup
- Consider if 2+ pregnancy losses or failed artificial reproduction cycles
History
- Prior pregnancies and childbirth: some men may have had prior children
- Ejaculate frequency: semen parameters peak after 1-2 days, then decline - no benefit in abstaining for long periods to "build up" semen
- Intercourse: timing, frequency
- Comorbidities: higher risk of infertility with HTN, HLD, obesity, DM, hypo/hyperthyroidism
- No association with infertility: caffeine, cell phones
Medical Causes
- TICS: Toxins, Infections/inflammation, Childhood history, Sexual history
- Neurologic: DM, SCI, and MS all affect normal ejaculation
- Cancer: can negatively affect sperm parameters even prior to treatment, testis cancer has even greater effect
- Hyperthermia: cryptorchidism, heated seats, and laptop heat should be avoided
- Infections: can cause strictures, prostatitis, testis failure, pre-pubertal mumps does not affect fertility, wait 3mo after febrile illness to check semenalysis
- Medical risk factors: liver failure, DM, thyroid disorders
- Hydrocele: increased prevalence in infertile patients but unclear cause and unclear benefit to performing hydrocelectomy
- Kartagener syndrome: nonmotile cilia prevent sperm motility, also have bronchiectasis, sinusitis, situs inversus, diagnose with evaluation of axoneme
- Young syndrome: thick epididymal secretions obstruct the vas, may also have bronchiectasis and sinusitis
- Cystic fibrosis: absent vas, bronchiectasis, sinusitis, pancreatic disease, evaluate with CFTR panel
- Congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens (CBAVD): isolated absence of vas (no URI symptoms)
Surgical Causes
- RPLND: results in retrograde ejaculation
- Hernia repair: can obstruct vas deferens or testicular blood supply, 1-2% vs 0.3% pediatric vs adult repair
- Pediatric inguinal surgery: testis atrophy develops in 0.3%
- Torsion: oligospermia (36-39%), antisperm antibodies (11%)
- Cryptorchidism: paternity rates 96% (unilateral) and 70% (bilateral), orchiopexy recommended before 10yo
Medication Causes
- Endocrine modulators: antiandrogens, spironolactone, HAART, steroids, estrogens, cimetidine, finasteride, allopurinol
- 5ARi: questionable effect on semen parameters, can consider stopping
- Anabolic steroids: inhibits LH, withdrawal can take months/years to reverse
- Illicit drugs: marijuana may decrease tesosterone, alcohol converts T to E, tobacco may affect sperm parameters, cocaine has questionable effects
- Antipsychotics: antidopamine effect leads to elevated prolactin
- Opioids: suppress LH at the hypothalamic level
- Chemotherapy: can lead to DNA damage at 2yrs after administration, mainly platinum-based, alkylating agents, antimetabolites, vinca alkaloids, topoisomerase inhibitors
- Antibiotics: tetracycline can be directly spermatotoxic, nitrofurantoin may have negative temporary effect
- Sulfasalazine: leads to oligoasthenospermai, can switch to mesalazine
- Environmental/Occupational exposure: heavy metals, pesticides, hyperthermia
Physical Exam
- Secondary sexual characteristics: pubic hair, gynecomastia, arm span > 5cm height
- Obesity: increased aromatase conversion to estradiol
- Genital exam: location/size of testes, presence of varicocele, palpable vas deferens, abnormal urethral appearance
- DRE: optional, SVs not normally palpable
Semenalysis
- Highly variable, check minimum 2 separated by 2-4 weeks
- Abstain from ejaculation for 24hrs (not more) to provide optimal sample
- Volume: consider workup if < 1.0-1.5mL
- Density: oligospermia (< 13.5million/mL) and cryptozoospermia (so few it's hard to measure)
- Total #: volume x density (normal > 39mil)
- Motility: asthenospermia (normal > 32%)
- Morphology: teratospermia (overabundance of abnormal forms), globospermia (lacking acrosomes) normal > 4%
- Vitality: necrospermia (large number nonliving sperm), normal > 58%
- Antisperm antibodies: due to injury of blood/testis barrier, suspect if sperm agglutination or decreased motility, seen in vasectomy, testis trauma, orchitis, cryptorchidism, testis cancer, varicocele
- Pyospermia: > 1million/mL, may cause injury secondary to reactive oxygen species, Pap smear will differentiate WBCs from immature germ cells
- Fructose level: > 13umol/ejaculate, low levels may indicated ejaculatory duct obstruction
Labs
- Not required for every patient
- Lab indications: obtain if concern for impaired libido, erectile dysfunction, oligozoospermia, azoospermia, atrophic testes, or abnormal physical exam
- Testosterone: normal > 280-300, 55+% should be bioavailable (check albumin + SHBG), peaks in the morning
- LH/FSH: sertoli dysfunction indicated by elevated FSH, testicular dysfunction indicated by elevated LH
- Estrogen: T/E ratio < 10 may indicate testicular dysfunction
- Prolactin: consider testing if infertility associated with visual field changes, headaches, or ED, repeat if elevated level (large variation)
- Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism: elevated LH/FSH with low T, indicates testicular dysfunction
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: low LH/FSH/T, indicates pituitary dysfunction
Diagnosing Infertility
Diagnoses (by semenalysis finding)
| Semenalysis finding | Further workup | Interpreting findings |
|---|---|---|
| Azoospermia (absent sperm) | Semenalysis | Low volume + acidic pH indicates obstruction |
| Testis size | Cutoff testis axis 4.6cm determines whether obstruction present | |
| Vas deferens | Absence indicates obstruction | |
| FSH | Cutoff 7.6IU/L determines whether obstruction present | |
| Karyotype + Y Microdeletion (if elevated FSH or testicular atrophy) | Kleinfelter and Y deletions are most common causes of non-obstructive azoospermia | |
| TRUS (if normal T and vas, obstruction suspected) | Confirm ejaculatory duct obstruction | |
| Low volume | History | Caused by DM, SCI, RPLND |
| Post-ejaculate urinalysis | Confirms sperm ending up in bladder | |
| Round cells > 1mil/mL | Special stains | Differentiate pyospermia from germ cells |
| Sperm agglutination | Antisperm antibody testing | ICSI may be indicated for ASA instead of IUI |
| Poor sperm mobility | Viability testing | Assess whether nonmotile sperm can be used for ICSI |
Adjunct Tests
| Test | Indication | If positive: |
|---|---|---|
| Post-ejaculate urinalysis | Low-volume ejaculate | Sperm retrieval |
| Karyotype | Nonoobstructive azoospermia | microTESE (for Kleinfelter) |
| Repeat pregnancy loss | Sperm aneuploidy - ICSI, adoption, donor sperm | |
| Y microdeletion | Nonobstructive azoospermia | Adoption (AZFa/AZFb) or ICSI (AZFc) |
| Transrectal US | Obstructive azoospermia + low volume/pH + normal T + palpable vas | TURED |
| CFTR gene panel | Absent vas deferens | Test female partner TESE |
| Sperm DNA fragmentation | Repeat IVF failure Repeat pregnancy loss |
TESE + ICSI |
| Antisperm antibody testing | Concern for obstruction, azoospermia, agglutination | Recommend ICSI Do not order if already planning ICSI |
| Scrotal US | Assess for varicocele in difficult scrotum (obese, high + tight) | Discuss clinical relevance of US varicocele |
| Abdominal imaging | Assess for malignant cause of new or nonreducible large right varicocele | |
| Renal US | Assess for renal absence if vas absent unilaterally (26-75%) or bilaterally (10%) | |
Diagnoses (by cause):
| Infertility Grouping | Diagnosis | Findings | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gonadotropin Dysfunction | Kallman syndrome | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Anosmia |
HCG + FSH, GnRH pump |
| Incomplete hypoandrogenism | Increased LH Decreased T |
Clomiphene/Tamoxifen Anostrozole/Letrozole |
|
| Pituitary tumors | Elevated prolactin MR imaging if prolactin elevated (> 50ug/L) |
Bromocriptine/Cabergoline Transsphenoidal surgery |
|
| Exogenous suppression | Specific hx steroids or other drugs | Stop offening agent(s) | |
| Testicular dysfunction | Kleinfelter (XXY) | azoospermia (92%) + small testes + hypergonadotropins mosaic in 10-20% |
microTESE + IVF/ICSI |
| Leydig cell (steroidogenic) dysfunction | Elevated LH Decreased T |
microTESE + IVF/ICSI | |
| Y Microdeletions | azoospermia (AZFa/AZFb) | Adoption, donor sperm | |
| oligospermia (AZFc) | microTESE + IVF/ICSI | ||
| Antisperm antibodies | secondary to blood/testis barrier breakdown | IVF/ICSI | |
| Varicocele | Physical exam | Surgical repair | |
| DNA Fragmentation | Assess after repeat IVF failure | TESE + ICSI | |
| Transportation Dysfunction | Absence of Vas Deferens | Physical exam findings History renal agenesis |
TESE + IVF |
| Congenital Bilateral Absence of the Vas Deferens (CBAVD) | CFTR mutation | CFTR screen panel TESE + IVF |
|
| Hypospadias Epispadias |
Physical exam findings | Intrauterine insemination | |
| Ejaculatory duct obstruction | Azoospermia + Hypovolemia TRUS findings (SV > 15mm AP, ED > 2.3mm) |
TURED | |
| Retrograde ejaculation | Azoospermia + Hypovolemia Sperm on post-ejaculate urinalysis |
Sperm retrieval (alkalinize with bicarb) Sympathomimetic agents (25% success) |
|
| Anejaculation | Neurologic history Prior RPLND |
Penile vibratory device Electroejaculation |
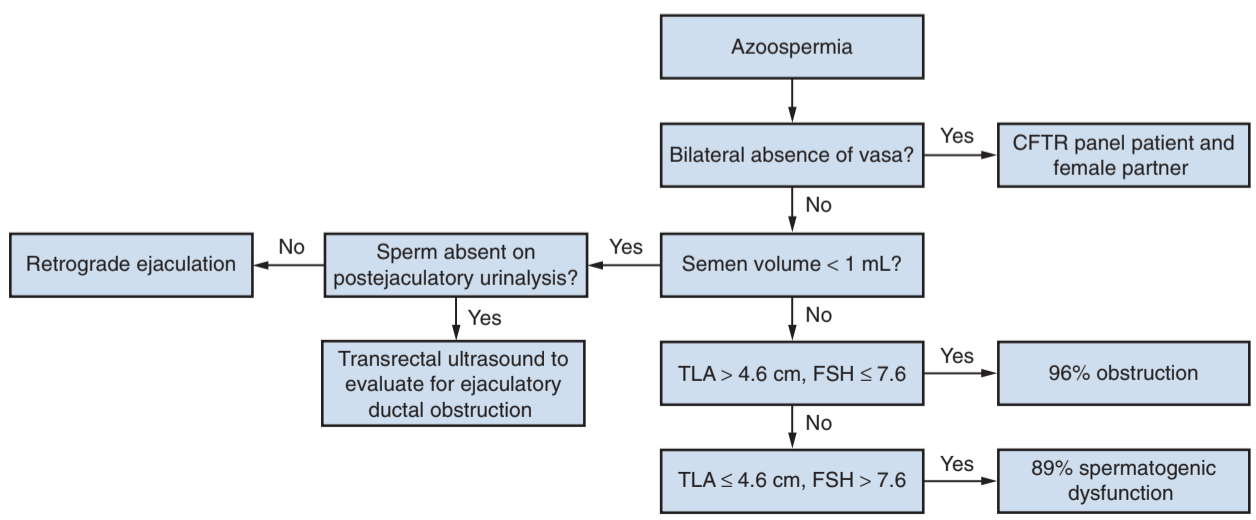
Azoospermia
- Obstruction: likely cause in 96% of patients with FSH < 7.6 and testis > 4.6cm
- Nonobstruction: likely cause in 89% of patients with FSH > 7.6 and testis < 4.6cm
- Biopsy: not indicated for initial workup, consider if indeterminate findings
Treatments
Medications
| Class | Medication | Dose | Indication | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonadotropin agonist | Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) | 1500-5000 IU 2-3x weekly Titrate up to 10K IU/week Titrate to T level |
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism | Nausea (12%) Breast enlargement/tenderness (1-10%) Headache (34%) Injection discomfort (1-10%) |
| Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (HMG) | 75-150 IU 2-3x weekly | |||
| Selective estrogen receptor modulator | Clomiphene citrate | 25mg QD or 50mg EOD Titrate to max 100mg QD Titrate to T level |
Headache (1%) Blurred vision (2%) Flushing (10%) Breast discomfort (2%) Nausea (2%) Impaired libido Gynecomastia (rare) |
|
| Aromatase inhibitor | Anostrozole | 1mg daily | Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (Kleinfelter syndrome) | Nausea (11-19%) Headache (9-10%) Hot flashes (12-26%) Chest discomfort (2-12%) |
| Lestrozole | 2.5mg daily | |||
| Dopamine agonist | Cabergoline | 0.25mg 2x weekly Titrate up to 1mg Titrate per prolactin levels |
Prolactin-secreting pituitary tumor | Headache (26%) Dizziness (15-17%) Nausea (27-29%) Constipation (7-10%) |
| a-agonist | Pseudoephedrine | 60mg PO QID | Retrograde ejaculation | restlessness Nausea/vomiting Weakness Headache Nervousness Dizziness Palpitations |
Varicoceles
- Prevalence: 15% all men, 40% subfertile men, more comon on L side, most common cause of infertility
- Grading scale (1-3): palpable with Valsalva only, palpable standing without Valsalva, visible on exam)
- Surgery recommended: palpable varicocele, infertility, and abnormal semen parameters
- Sugery maybe recommended: palpable varicocele and associated testis pain (may not improve/resolve), adolescent with varicocele + small testis (reverses testicular atrophy but may not prevent infertility)
- Surgery not recommended: non-clinically significant varicocele, even if scrotal/testis pain, non-obstructive azoospermia
- Success: pain improves in 50-90%, semen parameters improve in 70%, rates based on surgeon experience/technique, microsurgical has 1% recurrence rate and 0.4% hydrocele rate
- Varicocelectomy side effects: hematoma, hydrocele, edema, recurrence, atrophy, infection
Ejaculatory stimulation
- Penile vibratory stimulation: vibrator stimulates ejaculation in anejaculatory men, ejaculation reflex pathway must be intact, usually does not work in RPLND or SCI patients
- Electroejaculation: electrical current applied via transrectal probe, usually induces retrograde ejaculation (remove sperm from bladder), does not require ejaculation reflex, requires anesthesia (very painful)
Surgical treatment
| Class | Procedure | Indications | Description | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azoospermia diagnosis | Testis aspiration | Confirm obstructive (vs nonobstructive) azoospermia | Insert biopsy needle (thru skin or skin incision) and aspirate to assess for sperm | Hematoma, hematocele, spermatocele, hydrocele | Testis biopsy | Incise tunica albuginea, extrude tubules and remove, close incision | Low risk bleeding |
| Sperm retrieval | Tes(TESE) | Obstructive azoospermia | Obtain sperm via opening testis or epididymis and removing tubules | Bleeding, postop pain |
| microTESE | Nonobstructive azoospermia | Obtain sperm via assessing and extracting microtubules | ||
| Epididymal sperm extraction | Obstructive azoospermia with epididymal dilation | Obtain sperm via assessing and extracting microtubules | ||
| Improve sperm delivery | Vas reversal | Obstructive azoospermia (after vasectomy) | Obtain sperm via assessing and extracting microtubules | Hematoma (0.3%), granulomas (5%), delayed failure (5%), can consider TESE instead |
| Transurethral resection of ejaculatory ducts (TURED) | Obstructive azoospermia (ejaculatory ducts) | Resect ducts to remove obstruction, can transrectally inject dye to improve identification | Restenosis, pain, epididymoorchitis (chemical/infectious), retention, incontinence, hematuria | |
| Assisted reproductive technology | Intrauterine insemination (IUI) | Normal sperm but unable to reach egg naturally, oligospermia (5-8mil) | Inject collected/concentrated sperm into uterus (via cervix) to allow natural fertilization of egg | Minimal risks |
| In vitro fertilization (IVF) | Sperm unable to reach egg, oligospermia (< 5mil) | Sperm placed in proximity to egg, natural fertilization, embryos placed within uterus for implantation | Risks of egg stimulation/retrieval Multifetal pregnancy |
|
| Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) | Sperm unable to fertilize egg, oligospermia (< 5mil) | Sperm directly injected into egg, embryos placed within uterus for implantation | Risks of egg stimulation/retrieval 4x risk for sex chromosome abnormalities Congenital malformations (slight increased risk) Spontaneous abortion/ectopic pregnancy |
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Niederberger, C., S. Ohlander, and R. Pagani. "Male Infertility." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Schlegel, Peter N., et al. "Diagnosis and Treatment of Infertility in Men: AUA/ASRM Guideline." (2020).
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.