Priapism
Priapisms in General
Considerations and Causes
- Definition: erection > 4 hours beyond or unrelated to sexual stimulation
- Sickle cell: cause of 1/3 total cases worldwide
- ED therapies: priapism more common with ICI than with oral agents, 5% with titration in office, 0.4% with self-therapy, more common with papaverine and phentolamine than alprostadil
Workup
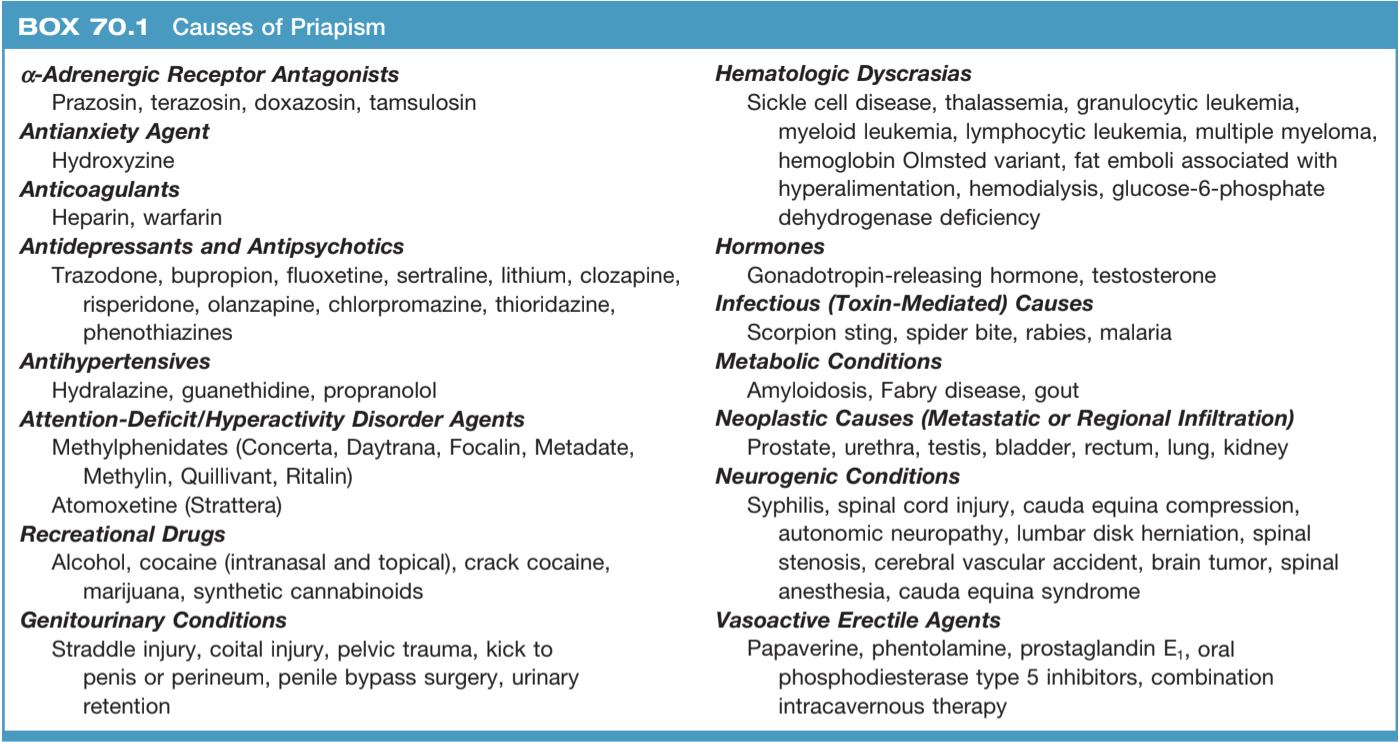
- Heme/Onc Hx: sickle cell, thalassemia, blood dyscrasia, malignancy
- Trauma: penile/perineal trauma, spinal cord injury
- Medications (prescribed): a-antagonists, anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin), hydroxyzine, hydralazine, propranolol, atomoxetine, ED agents
- Medications (psych meds): trazodone, bupropion, chlorpromazine, clozapine, fluoxetine, lithium, olanzapine, risperidone
- Medications (recreational): alcohol, cocaine, marijuana, amphetamines
- Medications (inpatient): TPN, IV contrast, spinal/general anesthesia
- Symptoms: duration, pain, prior priapism episodes and their treatments
- Labs: check penile blood gas and CBC, consider urinary toxicology screen and hemoglobin electrophoresis
- Doppler: only use if unclear whether ischemic or non-ischemic
- Thrombotic risk: increased risk for future cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events (per Mulloy 2023)
Ischemic Priapism
Evaluation/Diagnosis
- Definition: erection with little/no cavernous arterial inflow (compartment syndrome of the penis)
- Pain: common presenting symptom, takes 6-8hrs to develop
- ED risk: high risk (75-90%) of permanent erectile dysfunction after 24-36hr
- Penile blood gas: expect low pH (< 7.25), low oxygen (< 30), high CO2 (> 60)
Stuttering Priapism
- Most often seen in sickle cell patients (29-42% lifetime recurrence)
- Lab findings: anemia, elevated LDH, bilirubin, AST, reticulocytes, WBC, and platelets
- Immediate treatment: oxygenation, alkalinization, and exchange transfusion (discuss with hematology first), do not treat with cold application (can worsen sickle crisis)
- Commonly wakes patient up from sleep (occurs with nocturnal erections)
- Limited data: hydroxyurea, baclofen, gabapentin, terbutaline
- Do not start GnRH agonists or antiandrogens if patient has not completed puberty
Stuttering Priapism Treatment Options (from Hoeh 2014)
| Drug | MoA | Dose | Side Effects | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finasteride | 5ARi, prevents conversion of T to DHT | 5mg x40d, then 3mg x40d, then 1mg x40d Peds 1mg 1-2x daily x6mo |
Gynecomastia (uncommon) | Risk for ED, low libido |
| Sildenafil | increases cGMP (may be deficient in patients with recurrent priapism) | 25-50mg daily Take in AM, never before sex |
Headache, flushing, nasal congestion/rhinitis, dizziness | Do not take with nitrates |
| Ketoconazole | Inhibits testosterone production | 200mg TID + 5mg prednisone × 2 weeks, then 200 mg nightly without prednisone 200 mg nightly |
GI upset, gynecomastia, QT prolongation (rare), hepatotoxicity (rare) | Monitor LFTs |
| Pseudophedrine | Penile vasoconstriction | 30mg after priapism | HTN, tachycardia, diaphoresis, insomnia, cardiac arrhythmias (rare) | Treatment, not prevention |
| Phenylephrine | 100–500μg/mL, inject 1mL q3-5min for up to an hour until detumescence occurs | |||
| Leuprolide | GnRH agonist | 7.5mg IM monthly 45mg subQ q6mo |
Hot flashes, gynecomastia, loss of libido, ED, asthenia, osteoporosis | Limited use due to significant side effects |
Non-Surgical interventions
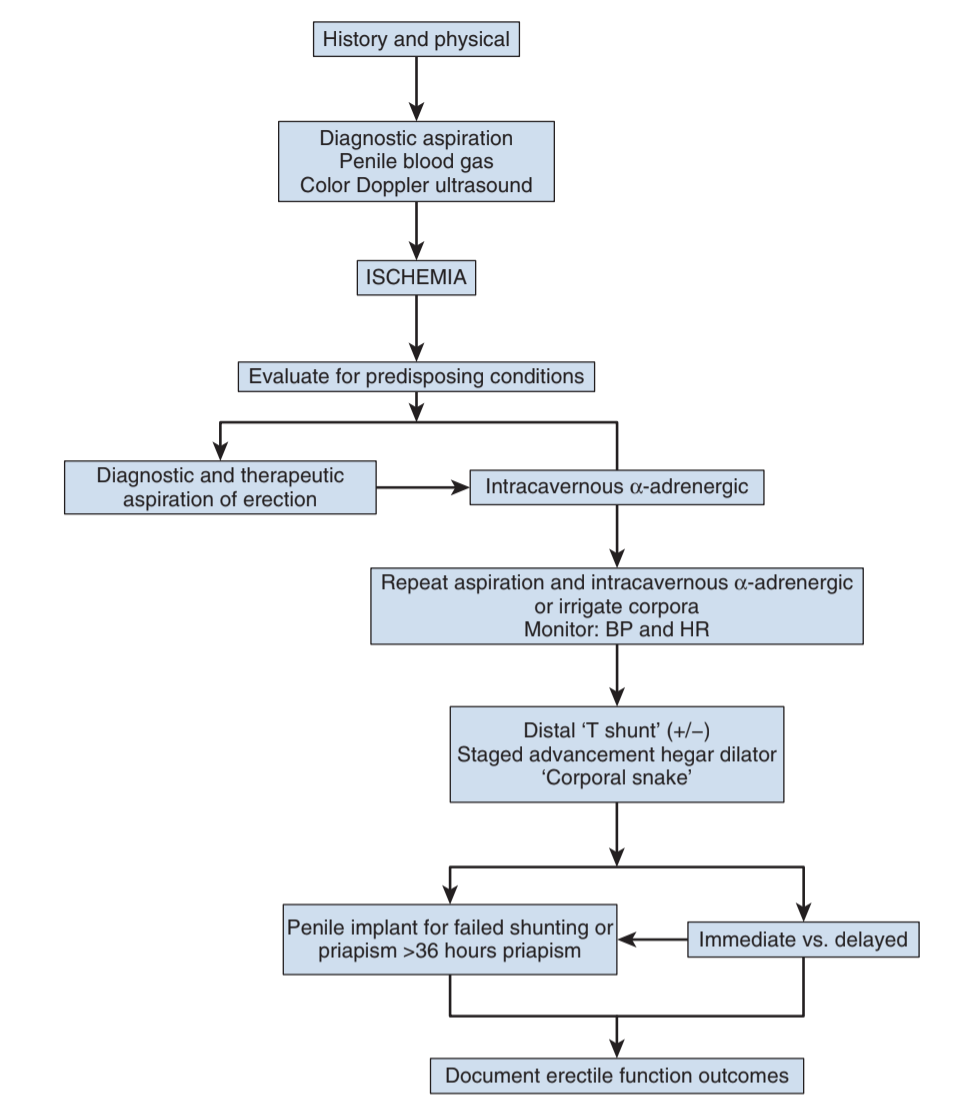
- Perform penile nerve block prior to aspiration/irrigation
- Aspiration: results in detumescence in 36%, aspirate until fresh blood visualized (not dark blood)
- Technique: aspirate with 19g needle at 3 or 9 o'clock to avoid neurovascular bundles, inject saline intermittently, cold saline works better (do not use in sickle cell patients)
- Phenylephrine: inject 100-200μg/mL with 1mL q3-5 minutes, to maximum dose 1mg, monitor BP while injecting to assess for hypertension and reflex bradycardia
- PO meds: pseudoephedrine and terbutaline have 28-36% efficacy, not recommended for acute management (potentially no better than placebo)
- After ICI: 200μm phenylephrine injection without aspiration (if < 4hr)
- Wrap with gauze + coban to prevent swelling and hematoma
Distal Shunts (general anesthesia recommended)
- Purpose: reoxygenation via relieving venous outflow, by creatining fistula between corpora and glans penis, will eventually close off
- Ebbehoj: straight incision (longitudinal) with #11 scalpel through glans into corpora
- Winter: place large-bore needle, angiocatheter, or Tru-cut needle through glans into corpora, reportedly least effective
- T-shunt: insert #10 scalpel longitudinally through glans into corpora, then rotate laterally (away from urethra) and remove, perform unilaterally then bilaterally if no resolution within 15min
- Al-Ghorab: 2cm transverse incision through glans distal to coronal sulcus and excision of tunica albuginea between glans and corpora
- Corporal snake: Perform Al-Ghorab, then insert 7/8 Hegar dilator through the tunical window
- Success: bright red blood aspirated, decreased intracavernosal pressure, penile detumescence and refilling, normal penile blood gas
- Tips: avoid compressive dressing, encourage squeezing to maintain patency, and consider anticoagulation (preoperative ASA 325 + SQH then ASA 81 x2 weeks)
- Complications: edema, hematoma, infection, conversion to high-flow, fistula, necrosis, and pulmonary embolism
Other options
- Proximal shunts: higher rates of erectile dysfunction and less preferred compared to distal shunt with tunneling
- Quackels: anastomose corpus to spongiosus, stagger on shaft if bilateral to prevent urethral stricture, can also cause fistula and cavernositis
- Grayhack: anastomosing saphenous vein to corpora, can lead to pulmonary embolus
- Barry: anastomosing deep dorsal vein to corpora
- Penoscrotal decompression: perform corporotomy similar to IPP placement, use pediatric Yankauer suction tip to remove clotted/fibrotic tissue (less destructive than actual IPP placement), can perform unilateral or bilateral
- Prosthesis placement: consider if shunts fail or prolonged priapism (> 36hr), avoids corporal fibrosis and preserves penile length (compared with delayed placement), potentially lower risk of infection, downside is need to make decision in immediate setting, higher risk of complications than average prosthesis patient, consider malleable placement (less complicated, less risk, can always convert to inflatable)
Other Priapisms
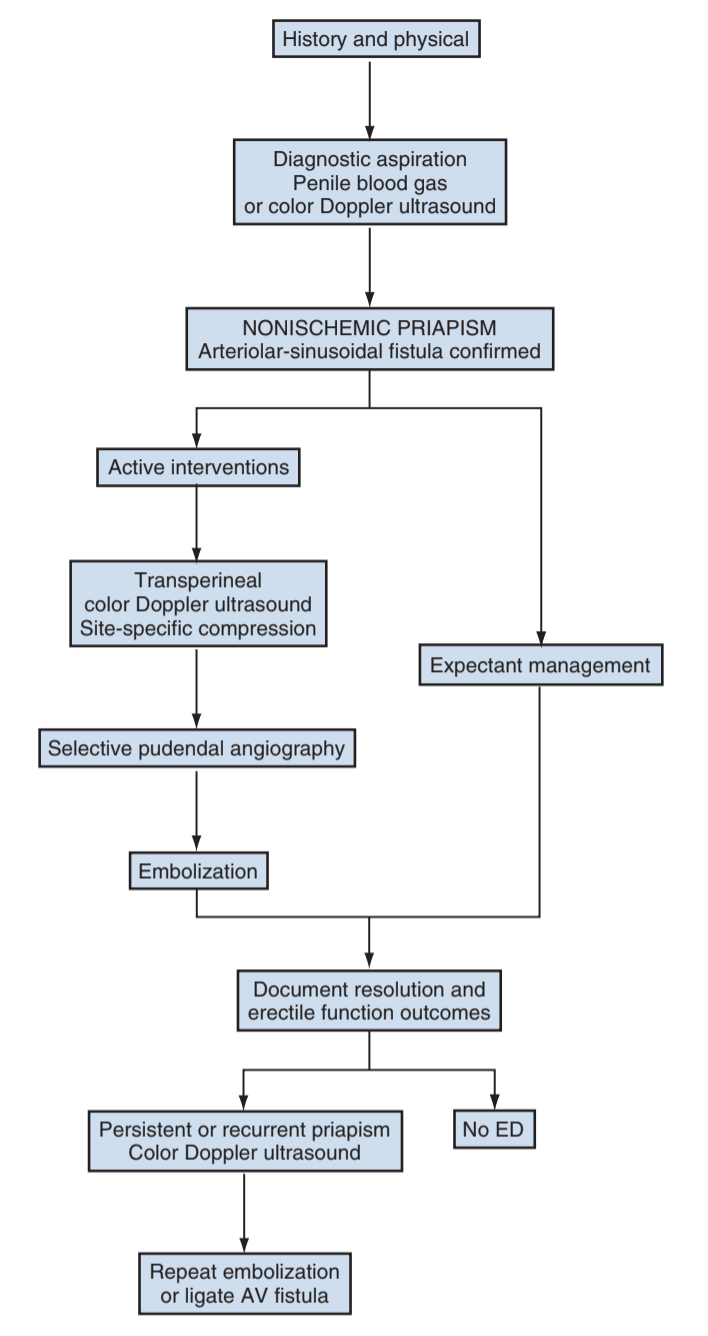
Non-ischemic priapism
- Definition: persistent erection from unregulated arterial inflow, but no hypoxia
- Presentation: no pain, usually report history of penile/perineal trauma
- Not an emergency, penis not ischemic
- Spontaneous resolution: up to 62% by 4 weeks of observation, can repeat US to assess for resolution
- Aspiration: only indicated for diagnosis, no benefit for treatment
- Selective embolization: indicated for immediate relief, demonstrates arteriolacunar fistula, embolize with agent of choice (non-permanent preferred), success rates 89-100%, erectile function rates 75-86%
- Ligation: not preferred, perform repeat embolization before considering ligation
Malignant Priapism
- Cause: most common with GU malignancy (69%), then rectal cancer
- Normal priapism management not effective or recommended
- Distal resection: consider if lesion can be completely resected
- Penectomy: consider for intractable pain, obtain MRI to assess proximal extent
- Other surgical therapies: dorsal nerve resection, SPT placement
- Radiation: usually unsuccessful
- Median survival 5-14 months
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Bivalacqua TJ, Allen BK, Brock G et al. "Acute Ischemic Priapism: an AUA/SMSNA Guideline."" J Urol 2022
- Broderick, G. "Priapism." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Hoeh, Michael P., and Laurence A. Levine. "Management of recurrent ischemic priapism 2014: a complex condition with devastating consequences." Sexual medicine reviews 3.1 (2015): 24-35.
- Mulloy, Evan, et al. "The risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in men with a history of priapism." Journal of Urology 209.1 (2023): 253-260.
- Pettaway, C., J. Crook, and L. Pagliaro. "Tumors of the Penis." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.