Urologic Use of Intestine
GI Anatomy
Gastric arteries
- Left gastric: arises from celiac, supplies lesser curvature
- Right gastric: arises from hepatic, supplies lesser curvature
- Gastroduodenal: arises from hepatic, supplies antrum and duodenum and gives off right gastroepiploic
- Splenic: arises from celiac, supplies fundus and cardia (short gastrics) and greater curvature (left gastroepiploic)
Jejunum vs Ileum
- Ileum has smaller diameter
- Ileum has more and smaller arterial arcades
- Ileum has thicker mesentery
Colonic watersheds
- Receive blood supplies from distal branches of two different vessels, vulnerable to ischemia
- Griffith's point: communication between middle and left colic arteries, perfuses splenic flexure
- Sudeck's point: communication between sigmoid and superior hemorrhoidal artery, perfuses superior rectum
Other notes
- If fundus used, should not include andrum, pylorus, or lesser curvature due to blood supply
- Pelvic XRT can injure last 2 inches of terminal ileum and 5ft of jejunum starting 6ft after ligament of Treitz (longest mesentery, may sit in pelvis)
- Concomitant bowel diversion: lower risk of postop complications if colonic conduit is used instead of ileal conduit requiring separate bowel resection (per Theva et al IBJU 2020 and Hagemans et al EJSO 2020)
Surgical planning
Choosing the right segment
| Segment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Stomach | Less permeable to solutes Produces less mucus Less risk for metabolic acidosis (CKD) |
Hyperkalemic hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis Hematuria/Dysuria syndrome Dumping syndrome B12/Iron deficiency |
| Jejunum | None | Hyperkalemic hypochloremic metabolic acidosis, hyponatremia |
| Ileum | Mobile Small diameter Constant blood supply |
Hypokalemic hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis B12 deficiency Bile salt diarrhea Fat malasorption |
| Colon | Able to reach anywhere in abdomen/pelvis Less likely to have been irradiated Less risk for metabolic abnormalities |
Hypokalemic hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis Needs mobilization Diarrhea with removal of ileocolic valve Cancer risk |
Preoperative workup
- Prior intestinal surgery: further resection may compromise blood supply, consider using stomach if short gut syndrome
- Prior pelvic XRT: may make some segments unusable, transverse colon or stomach preferred
- Colon contraindications: diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis
- Check manual dexterity if considering a catheterizable diversion
- Assess renal and hepatic function (affected by solute reabsorption)
Principles of intestinal surgery
- Adequate intestinal exposure
- Maintain good blood supply
- Avoid local spillage of enteric contents
- Maintain serosa/serosa anastomosis
- Do not strangulate tissue
- Realign mesentery
Neurogenic bladder options
- Enterocystoplasty: indicated for poor bladder compliance, reduced capacity, significant DO
- Catheterizable channel: avoids drainage bag, increases continence, allows more freedom, and improves body image, options include Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy, Yang-Monti ileal tube, tapered ileum, ileocecocystoplasty
Non-orthotopic urinary diversion options
- Ileal conduit: simplest conduit, avoid if IBD or prior XRT
- Kock pouch: continent reservoir using ileum, requires nonrefluxing nipple valves for ureters and stoma
- Mainz and Indiana pouches: use of terminal ileum and cecum to create catheterizable pouch, requires ileocecal valve usage
Orthotopic neobladder
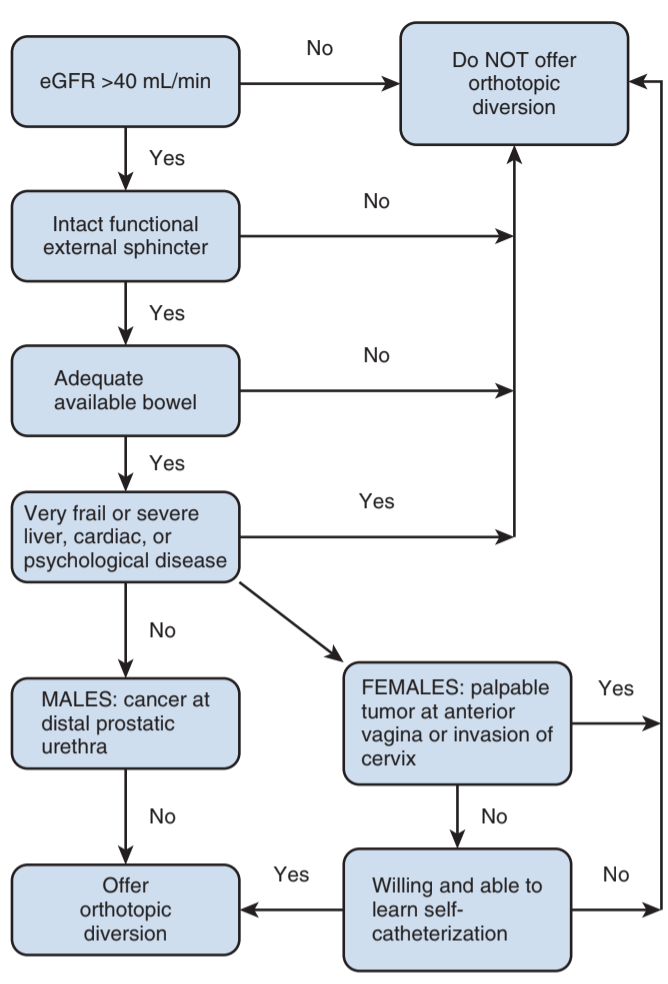
- Necessary criteria (for both neobladder and continent diversion): eGFR > 35-40 (Cr < 1.7-2.2), functional external sphincter, adequate bowel length, no severe medical comorbidities (esp renal/hepatic), no distal urethral cancer, willing/able to self-catheterize
- No relevance to neobladder placement: CiS, prior XRT, high risk for recurrence, age, obesity
- Detubularize bowel to provide volume 300-500mL at maturity
- Varieties include Studer, Hautmann, Mainz neobladder
- 4-25% develop retention and require longterm CIC
- Neobladder not recommended in setting of metastatic bladder cancer - cannot give adjuvant XRT if neobladder present, and recurrences can erode into neobladder
Stoma tips
- Use flush stomas for catheterizable channels, protruding stomas for appliances
- Mark stoma with patient sitting and supine, place over rectus muscle 5+cm away from incision, place at peak of infraumbilical fat roll place away from creases or scars
- AUA/WOCN Stoma Marking Joint Position Statement
Ureterointestinal anastomosis
- No evidence that refluxing anastomosis causes longterm renal damage
- Avoid extensive ureteral mobilization, ensure watertight mucosal anastomosis
- Bricker: refluxing, end to side anastomosis, ureters anastomosed separately
- Wallace: refluxing, end to end anastomosis, ureters anastomosed together first then anastomosed to intestine
Complications
General intestinal complications
- Renal deterioration: 13-18% have deterioration
- Metabolic abnormalities: depends on intestinal segment utilized
Anastomotic complications
- Fistula: fecal (4-5%) w/ 2% mortality, neobladder/vaginal 11%
- Infection: up to 45% have some form of infectious complication, 10% wound complication risk, sepsis 4% w/ 17% mortality
- Bowel obstruction: 10% when stomach or ileum used, 5% for colon, adhesions is most common cause, can be caused by cancer recurrence
- Hemorrhage: can be caused by anastomotic ulcers along suture line
- Stenosis: caused by temporary edema, ischemia, infection, or surgical errors
- Pseudoobstruction (Ogilvie syndrome): dilated cecum immediately postoperatively, 23% rupture risk with diameter > 12cm or rising WBC level, treat with neostigmine or endoscopic decompression
- Leak: seen in up to 1-2%, manage depending on situation
Intestinal segment complications
- Stricture: lymphoid depletion leads to persistent infection and subsequent scarring
- Elongation: caused by distal obstruction, can lead to renal failure
- Infection: colonization with Proteus or Pseudomonas increases risk for upper tract deterioration
- Stones: increased risk for struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) stones 3-20% depending on conduit type
- Cancer: can take 10-20yrs to develop, due to urine exposure to intestine and fecal exposure to GU epithelium, low < 1% risk with ileal neobladder or conduit
- Mucus production: can increase with dairy product ingestion, may require regular irrigation to clear mucus and prevent stone formation, can irrigate with N-acetylcysteine (10-20% solution) or urea (30-50mL of 20-40%)
Stoma complications
- Avoid with ostomy nursing care, skin care, nonirritative adhesives, acidic urine, and proper device fitting
- Stenosis: 20-24% with ileum and 10-20% with colon, ensure proper appliance fitting
- Stenosis intervention indications: pain, infection, retention, hydronephrosis, difficulty catheterizing
- Stenosis treatment (from hernia): hernia support belt, surgical repair, indwelling catheter
- Stenosis treatment (no hernia): periodic dilation, surgical revision, indwelling catheter
- Parastomal hernia: 1-4%, ensure adequate placement through rectus without overdilating fascia
Ureterointestinal anastomotic complications
- Stricture: caused by ischemia, urine leak, XRT, or infection, more common on L side, decreased with soft silicone stents, endoscopic management successful in 50-60%, surgical repair success higher
- Fistula: 3-9%, occurs within 7-10 days of surgery, decreased with soft silicone stents, can lead to fibrosis and scarring
- Leak: seen in up to 5%, requires maximal urinary drainage away from leak site (catheter/PCNs)
Metabolic complications
- Stomach: hypochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis (loss of H+ and Cl-), worse with renal failure, can use H2 blockers or PPI, but may need to remove segment
- Jejunum: hyponatremic hypochloremic hyperkalemic metabolic acidosis (loss of Na+ and Cl-), hydrate and alkalinize
- Ileum/colon: hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, may have total body potassium depletion, supplement citrate or bicarbonate, chlorpromazine (25-50mg TID) and nicotinic acid (400mg TID-QID) inhibit cAMP and chloride transport
- Delirium: can be due to hypomagnesmia or ammonia toxicity
- Drug toxicity: may be due to unmetabolized drugs becoming excreted in urine and reabsorbed by bowel segment
- Osteomalacia: due to acidosis, Vitamin D resistance, and renal calcium loss, treat by resolving acidosis and supplementing calcium and Vitamin D
- Malabsorption: may have bile salt, calcium, folic acid losses
- B12 deficiency: 8% risk at 15yr, start checking B12 at 5yr after surgery, give 2000ug daily PO, 25% will eventually require IV supplementation
- Diarrhea: often from bile salt malabsorption, more likely if ileocecal valve removed, can lead to significant fecal incontinence in < 3%, treat with cholestyramine 4-8mg BID and/or loperamide (Imodium)
Neobladder complications
- Urine leak: preferable to place drain and PCNs, open repair not recommended during immediate postoperative period
- Retention: perform cystoscopy to rule out stricture or tumor recurrence, manage with CIC
- Daytime incontinence: improves over 6-12mo, increased risk with age > 65, DM, lack of nerve-sparing, may require bulking agents or slings
- Nighttime incontinence: occurs in up to 50%, due to lack of feedback, decreased sphincter tone, decreased urethral sensitivity, may need to wake up 2-3x nightly to empty neobladder
- Infection: more common with poor emptying, assess for stones/obstruction
- Stricture: urethral anastomotic strictures rare
- Stones: more likely if staples used
- Vaginal fistula: decrease risk with omental flap
- Rupture: rare as outlet resistance is usually low, higher risk if prior XRT or chronic retention, diagnose with cystogram
Augment complications
- Infection: evaluate CIC technique or voiding diary (if spontaneously voiding), consider treating all urea-splitting organisms (can lead to stones), ensure CIC ≥ 4x daily, consider daily saline irrigation (240mL), consider gentamicin irrigation
- Acidosis: usually insignificant if normal renal function, consider bicarb/citrate supplements if bicarb < 21, supplement Calcium and Vitamin D to prevent renal osteodystrophy
- Bladder stones: 13-36% at 10yr, less likely if CIC via urethra (vs channel), can be treated via open or percutaneous or endoscopic approach, prevent with weekly saline and/or gentamicin irrigation, 15-30% recur within 2yr
- Kidney stones: increased risk for sepsis after treatment, 80% grow different organisms on stone culture vs preop urine culture
- Perforation:3-6% at 10yr, more likely if prior bladder neck closure and detubularized segments, risk factors include alcohol use, infections, and bowel ischemia, diagnose with clinical picture and low-pressure cystogram, managed surgically
- Renal failure: higher risk if GFR < 45, prevent with overnight catheter drainage if GFR < 50
- Malignancy: rare (0-4%, > 90% occur > 10yr after augment), risks include gastric augment, tobacco use, immunosuppression, prior exstrophy, rapidly growing (diagnosed 4-18mo after normal cystoscopy), 75% mortality within 15mo, no benefit to annual screening cystoscopy, consider cystoscopy if frequent UTI, gross hematuria, chronic pelvic pain, or colonic augment at > 50yo
- Pregnancy:
- Surveillance: annual history, physical, renal US, BMP, UDS and cystoscopy only in select cases
Catheterizable channel complications
- Prolapse: 2-5%, can try silver nitrate application, resection/repair may cause channel incontinence
- Incontinence: 1-47%, worsens during puberty and obesity, assess cause with urodynamics (stress leakage vs NGB), can manage with increased CIC, anticholinergics, botox, bulking agents, detrusor wrapping/bulking, augmentation
- Stenosis/stricture: ischemia may occur as bladder shrinks and abdominal thickness increases, prevent with overnight catheter or L-stent, can manage with stopper + topical steroids, steroid injections, dilation (high recurrence rates), superficial repair (YV, VQZ), stoma relocation (at skin or bladder), increase length with Monti + APV
- Revisions: 18-58%, more likely with Monti compared to APV (natural lumen, long mesentery, no suture line)
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Boone, T., J. Stewart, and L. Martinez. "Additional Therapies for Storage and Emptying Failure." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- DeCastro, G., J. McKiernan, and M. Benson. "Cutaneous Continent Urinary Diversion." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Hagemans, J. A. W., et al. "Outcomes of urinary diversion after surgery for locally advanced or locally recurrent rectal cancer with complete cystectomy; ileal and colon conduit." European Journal of Surgical Oncology 46.6 (2020): 1160-1166.
- Skinner, E. and S. Daneshmand. "Orthotopic Urinary Diversion." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Theva, Didi P., et al. "Concurrent urinary and bowel diversion: Surgical modification with sigmoid colon that avoids a bowel anastomosis." International braz j urol 46 (2019): 108-115.
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.
- Wintner, A. and D. Dahl. "Use of Intestinal Segments in Urinary Diversion." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).