Upper Tract Abnormalities
Cystic Renal Diseases
| Disease | Inherited? | Renal Findings | Non-renal Findings | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARPKD | Yes (chromosome 6) |
Large homogenous echogenic kidneys | Hepatic fibrosis Biliary dysgenesis |
Respiratory support May require nephrectomy due to compression Splenorenal shunt for portal HTN |
| ADPKD | Yes PKD1: 16 PKD2: 4 PKD3: not mapped |
Cysts throughout renal parenchyma | Diverticulitis Liver/spleen/pancreas cysts Mitral valve prolapse Intracranial aneurysms Seminal vesicle cysts (40%) |
Control HTN (ACE/ARB) Consider cyst drainage |
| Juvenile nephronophthisis Medullary cystic kidney disease |
Yes (chromosome 2) |
Corticomedullary junction cysts | Retinitis pigmentosa (16%) Hepatic fibrosis |
Sodium repletion |
| Tuberous sclerosis | Yes TSC1: 9 TSC2: 16 |
Cysts + AMLs RCC (3%) |
Epilepsy (80%) Facial angiofibromata (75%) Developmental delay (60%) |
Consider AML removal if > 4cm |
| VHL | Yes (chromosome 3) |
Cysts (76%) + adenomas RCC (35-38%) |
Cerebellar hemangioblastomas Retinal angiomas Pheochromocytomas (10-17%) Pancreas/epididymis cysts |
Partial nephrectomy for cancer control Conisder bilateral nephrectomy |
| Multicystic dysplastic kidney | No | Minimal nephron development Diffuse cysts |
Nephrectomy for pain/hemorrhage | |
| Benign multilocular cyst | No | Normal kidney compromised by growing cystic mass | Partial/radical nephrectomy | |
| Simple cyst | No | Single/multiple cysts More common with increasing age |
Depends on Bosniak classification | |
| Medullary sponge kidney | No | Ectatic collecting ducts Normal nephrons |
KCit for stones Abx ppx for recurrent UTIs |
|
| Acquired renal cystic disease | No | Diffuse cysts Occurs with ESRD |
Excision if mass > 3cm |
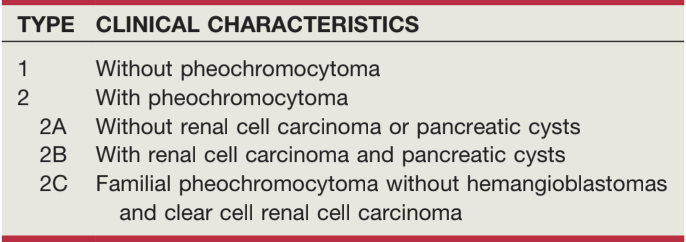
Von Hippel-Lindau classification, from Campbell's
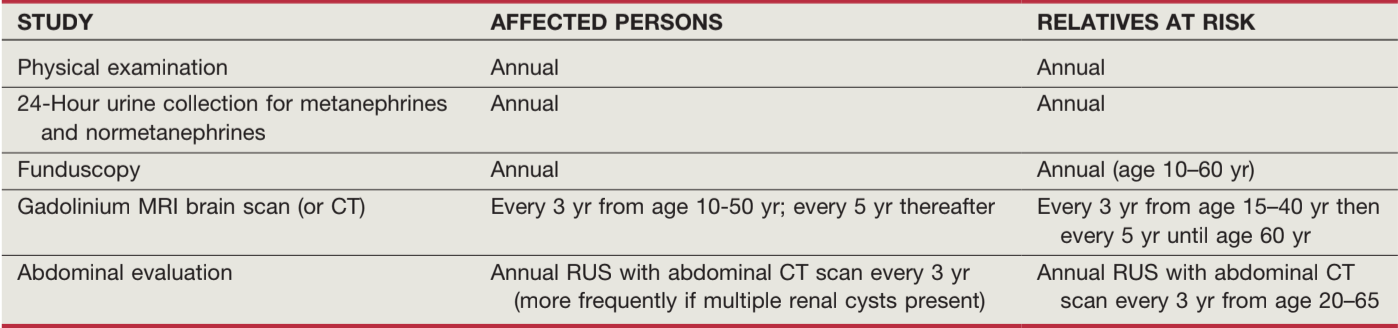
VHL screening for patients and family, from Campbell's
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
- Hematuria presenting sign in 19-35%
- Stones develop in 20-30%
- EPO levels increased, anemia is unusual
- HTN present in 50% 20-35yo, 100% with ESRD
- Intracranial aneurysm present in 10-30%, will cause subarachnoid hemorrhage (sudden severe headache) -> death in 9% of this subgroup, prevent by treating HTN
- Obtain family hx (3 generations) - assess renal disease, HTN, and strokes
- US diagnostic criteria (if family risk): 2+ cysts if < 30yo, 2 cysts per kidney if 30-59yo, and 4 cysts per kidney if > 60yo
- If no family history, diagnose based on bilateral renal cysts and 2+ associated findings: bilateral renal enlargement, 3+ hepatic cysts, cerebral artery aneurysm, solitary cyst of arachnoid/pineal/pancreas/spleen
- Cyst infection: treat with lipophilic antibiotics (bactrim, quinolones, chloramphenicol)
- Aneurysm screening recommendations: family hx aneurysm or SAH, prior naeurysm rupture, preop for major elective surgery, high-risk occupation, or high anxiety regarding potential aneurysm
- Aneurysm management: conservative therapy if < 7mm, otherwise treat (2% risk rupture per year)
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
- Usually apparent at birth, if not will become apparent by age 13-20
- 50% die after birth, another 25% by 1yo
- All patients have hepatic fibrosis and biliary ectasia
- Increased echogenicity on renal US due to microcysts
Juvenile Nephronophthisis (NPH) and Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease (MCKD) Complex
- Similarities: cause polydipsia/polyuria, histologic triad (irregular basement membrane thickening/disintegration, tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis)
- Juvenile NPH: autosomal recesive, no HTN, renal failure by 25yo, extrarenal symptoms
- MCKD: autosomal dominant, HTN, renal failure by 50yo
Tuberous Sclerosis
- Diagnosis: 2 major features or 1 major + 2 minor
- Major features: renal AML, facial angiofibromas, ungual/periungual fibromas, 3+ hypomelanotic macules, shagreen patch, multiple retinal hamartomas, cortical tuber, subependymal nodule, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, cardiac rhabdomyoma, lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Minor features: multiple renal cysts, nonrenal hamartoma, hamartomatous rectal polyp, retinal achromic patch, cerebral white matter radial migration tracts, bone cysts, gingival fibromas, enamel pits, "confetti" skin lesions
- Renal AML seen in 40-80%, common after 10yo
- Renal cysts in 20%, usually appear by 3yo
- AML management: embolize or excise if > 4cm to prevent spontaneous hemorrhage, otherwise screen with annual renal US or CT
- Surgical indications: > 4cm, pain, bleeding, compromising renal function, concern for RCC
- EXIST-2 trial: patients with TSC or LAM and AML 3+cm, treated with everolimus 10mg daily vs placebo, 4% AML progression (vs 21%), 50% reduction in size in 42% (vs 0%), improvement in skin lesions (26% vs 0%), but risk of stomatitis and acne-lesions
Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)
- If family history, diagnosis made based on presence of hemangioblastoma, RCC, or PCC
- If no family history, need 2+ "cardinal" manifestations
- Consider partial nephrectomy vs bilateral nephrectomy for cancer control
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney (MCDK)
- Multiple cysts of different sizes without normal parenchyma and no renal function
- Second most common cause of newborn abdominal mass (after hydronephrosis), most common cause of renal cystic disease
- Atretic ureter and hypoplastic renal vessels
- Contralateral abnormalities: UPJO (3-12%), VUR (18-43%)
- 40% will spontaneously involute
- No association with HTN or neoplasms
- Usually diagnosed on prenatal US and confirmed after birth, cysts are different sizes and no communication (UPJO shows similar sized cysts/calyces with some connectoin)
- DMSA/MAG3: MCDK shows minimal/no function, hydronephrotic kidney will show some function
- Surveillance: some recommend annual BP check, screening renal US at 1yr and 6yr, consider nephrectomy if HTN develops or kidney enlarging
Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK)
- Distal ductal dilation and diverticula, confined to medullary pyramids
- CT urogram or IVP are best for diagnosis: enlarged kidneys, papillary calficiations, elongated tubules filling with contrast, papillary contrast blush with persistent medullary opacification
- Usually asymptomatic, may present with colic, UTI, or hematuria
- Differentiate from ADPKD - no liver cysts, no cortical cysts, no family history
- Medullary nephrocalcinosis may be present, but differentiate from other causes based on difference in collecting duct caliber (normal vs dilated)
- Potassium citrate often used for hypercalciuria and hypocitraturia
- May require antibiotic prophylaxis if recurrent infections
Benign multilocular cyst (Cystic nephroma)
- Benign end of spectrum ending with cystic Wilms tumor (children) or cystic RCC (adults)
- Usually diagnosed before 4yo (2:1 M:F) or after 30yo (1:8 M:F)
- Asymptomatic flank mass in children, flank mass with pain/hematuria in adults
- Will have compressed normal parenchyma, MCDK has no normal parenchyma
Acquired Renal Cystic Disease
- 3+ cysts in each kidney in ESRD patient, seen with both HD and PD, likely caused by uremia
- RCC: 3x more likely if cysts present, 6x more likely in large vs small cystic kidneys
- If uremic + febrile, consider cyst infection - may require percutaneous drainage
- Persistent bleeding/pain: embolization or nephrectomy
- If HD for 3+yrs, screen with US q6mo if no cysts/tumors or CT+US q6mo if cysts/tumors < 2cm identified
- If tumor > 3cm, recommend surgical removal
Congenital nephrosis
- Similarities: proximal tubule dilation, severe proteinuria
- Finnish type: autosomal recessive, proteinuria present at first UA, 50% mortality by 6mo, (100% by 4yo), treated with transplant
- Diffuse mesangial sclerosis (DMS): 100% ESRD by 3yo, 1/3 associated with Denys-Drash syndrome (nephrotic syndrome, Wilms tumor, +/- DSD)
Other diseases
- Cortical microcystic disease: stable/progressive renal failure, small/normal kidneys with irregular cayces and papillae, family history, glomerular cysts
- Calyceal diverticulum (pyelogenic cyst): outpouching of collecting system, can develop stones
- Parapelvic cyst: parenchymal cyst impinging on renal pelvis, usually asymptomatic and diagnosed incidentally
- Renal sinus cyst: arises from lymphatics or adipose, not renal parenchyma
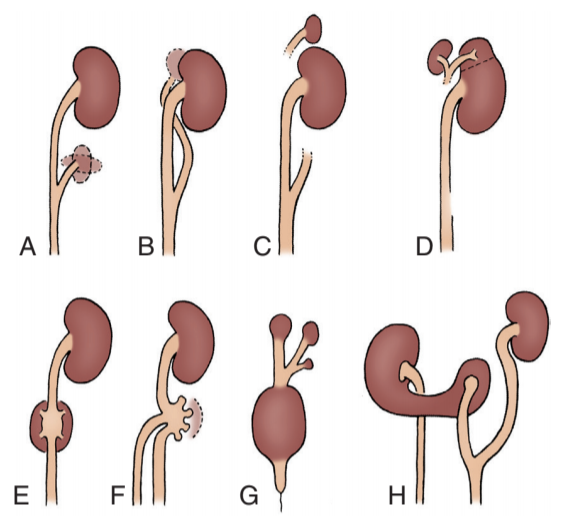
Variety of supernumerary kidneys with one ureter, from Campbell's

Variety of supernumerary kidneys with two ureters, from Campbell's
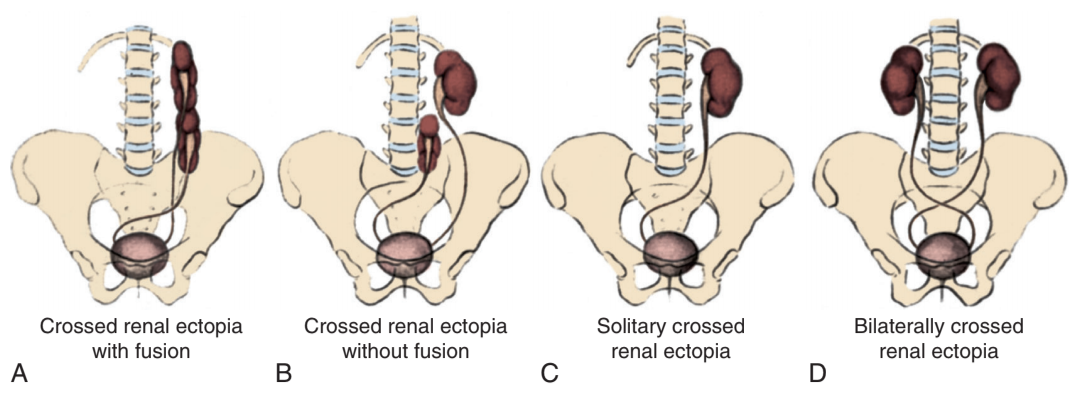
Variety of crossed ectopia, from Campbell's
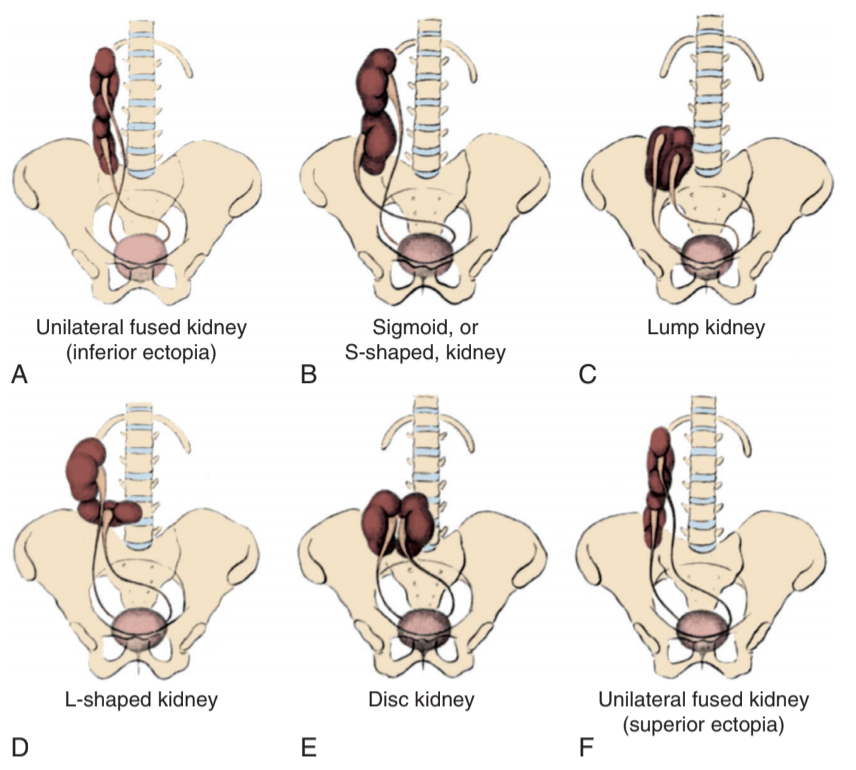
Variety of cross fused ectopia, from Campbell's
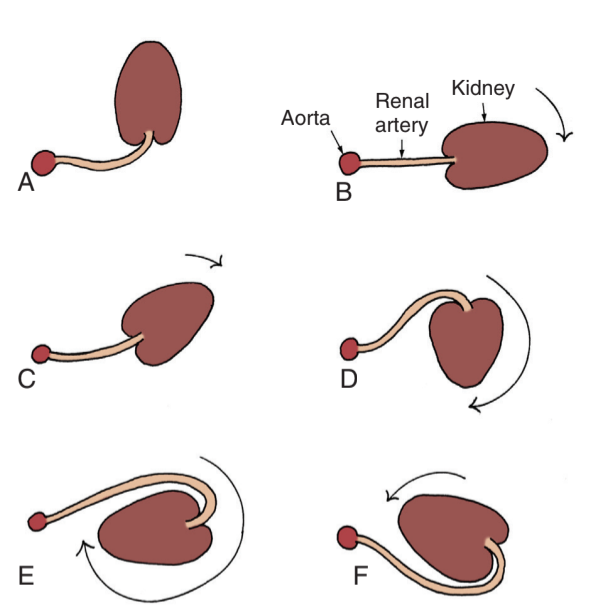
Malrotation: A embryonic, B normal, C incomplete, D hyper, E hyper, F reverse, from Campbell's
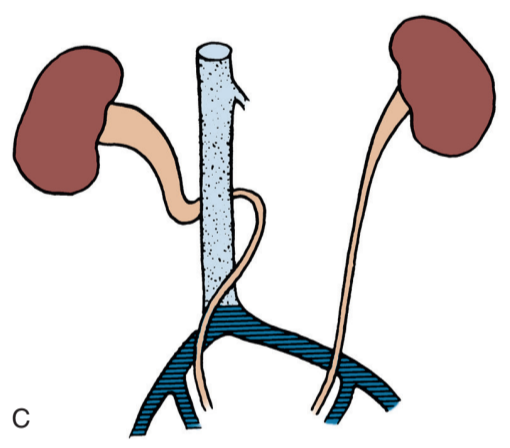
Retrocaval ureter, from Campbell's

Anterior-posterior diameter determination of antenatal hydronephrosis, from Campbell's
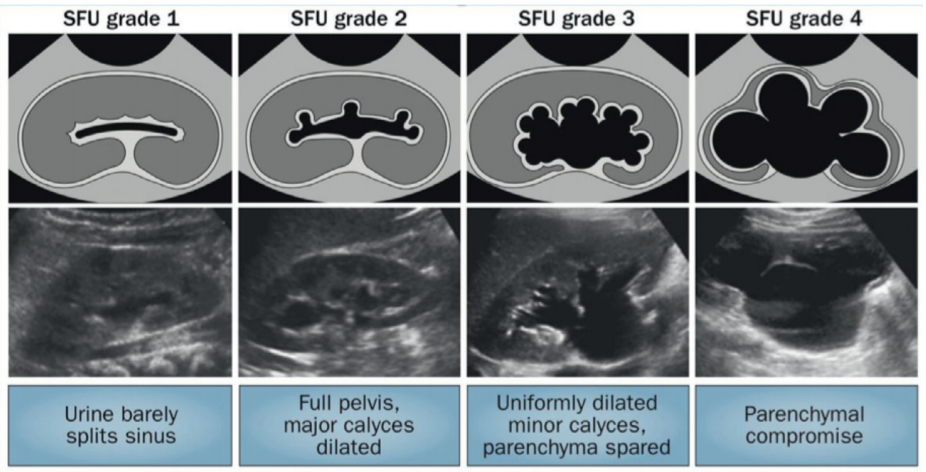
SFU grading of antenatal hydronephrosis, from Campbell's
Renal Anomalies
Abnormal renal number
- Bilateral renal agenesis: rare (500 cases) and almost always incomplatible with life
- Unilateral renal agenesis: ureter absent in 60%, GU anomalies in 25-50% women (10-15% men), 50% men have absence of vas deferens, can perform VCUG (28% contralateral reflux), no sports restrictions, recommend BP and microalbuminuria checks 1-2x yearly to screen for renal disease, women should have pelvic US to screen for Mullerian abnormalities
- Supernumerary kidney: rare, incidentally diagnosed, usually asymptomatic
Renal dysplasia
- Renal dysgenesis: main cause of pediatric ESRD, renal US shows small, hyperechogenic kidneys, loss of corticomedullary and parenchymal/perirenal fat distinction, may have cysts
- Hypoplasia: decreased number of calyces and nephrons
- Oligomeganephronia: decreased number of nephrons but hypertrophy of each nephron
- Ask-Upmark kidney: acquired reflux nephropathy leads to segmental renal hypoplasia, patients have severe HTN, imaging shows slit scars on kidney, nephrectomy may treat unilateral disease
Renal ascent and fusion anomalies
- Simple ectopia: usually demonstrates incomplete rotation, hydronephrosis common, may be more likely to form stones and higher risk for trauma due to lack of protection, can be found pelvic or thoracic
- Crossed ectopia: 90% are fused to contralateral kidney, ureteral orifice usually orthotopic (ectopic UO 3%), VUR seen in 20% (71% if bilateral crossed ectopia), stone pain lateralizes to origin, pyelonephritis lateralizes to current location
- Horseshoe kidney: 95% fused at lower pole, pelves usually anterior, IMA usually blocks full ascent, isthmus usually parenchymal, ~13% develop pyelo and ~17% develop stones
- Malrotation: more common in Turner syndrome, may develop hydronephrosis
Calyceal abnormalities
- Diverticulum: epithelial lined cavity with isthmus, usually asymptomatic but 40% present with stones, can follow with US if asymptomatic, can treat stones and ablate lining if symptomatic
- Hydrocalycosis: dilation of a major calyx, rare
- Megacalycosis: nonobstructive calyceal enlargement related to malformation of renal papillae, may also have increased number, usually asymptomatic
- Infundibulopelvic stenosis: dysmorphic kidney with degrees of stenosis, need treatment to protect renal function
Vascular anomalies
- Accessory vessels: 15-29% have accessory artery, lower pole is most likely to have accessory vessel, occasionally cause UPJO
- Renal artery aneurysm: usually asymptomatic (especially in children), may present with pulsatile abdominal mass or bruit, 18% rupture risk if > 3cm, treat if > 3cm or > 2cm and asymptomatic
- Arteriovenous fistula: can be acquired (trauma, biopsy, surgery), may be secondary to aneurysm eroding into vein, can cause renal ischemia and hypertension, treat with embolization or surgery once diagnosed
- Retrocaval ureter (preureteral cava): right ureter crosses behind vena cava, due to failure of subcardinal vein to atrophy during development, contrast studies (CTU/MRU/RGPG) help delineate ureteral path, treated with ureteral division and reanastomosis (may need to resect aperistaltic segment)
Prenatally diagnosed urinary tract dilation (UTD)
- Seen in 1-3% fetuses
- UTD grading systems: anterior/posterior renal pelvic diameter (APRPD), SFO, and UTD
- If SFU 1-2 (UTD A1) detected before 28 weeks, repeat US at 32 weeks
- If SFU 3-4 (UTD A2-3) detected before 28 weeks, repeat US every 4 weeks
- SFU resolution: 100% Grade 1 resolve within 30 months, 90% Grade 2 resolve within 48 months
- Antibiotic prophylaxis: no clear recommendation, can consider for P3 or high risk patients, can give until VCUG rules out reflux
- if concern for GU anomaly, obtain US 48hrs after birth
Postnatal hydronephrosis management
| SFU Grade | If... | Then... |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1-2 | Newly diagnosed | Renal US in 1-6mo |
| Grade 3 | Renal US in 1-3mo | |
| Grade 4 | Renal US + VCUG + renal scan in 1-3mo | |
| Grade 1-2 | Hydronephrosis resolved | Follow up PRN |
| Hydronephrosis stable | Renal US q6-12mo until resolved or toilet trained | |
| Hydronephrosis after toilet training | Space out or stop renal US | |
| Grade 3 | Improving hydronephrosis | Renal US q6-12mo until resolved |
| Stable hydronephrosis | Renal US q3-12mo until resolved | |
| Worsening hydronephrosis | VCUG + renal scan | |
| Grade 4 | Improving hydronephrosis | Renal US q3-12mo until resolved |
| Stable hydronephrosis | Renal US q3-6mo | |
| Worsening hydronephrosis | Pyeloplasty | |
| Split function < 30-40% | ||
| Worsening renal function | ||
| UTIs | ||
| Stable hydronephrosis + renal function > 40% | Pyeloplasty vs surveillance |
Ureteral anomalies
Ureteral duplication
- Common, seen in 0.8% people
- Weigert Meyer rule: lower pole refluxes (VUR/UPJO), upper pole obstructs (ectopic/ureterocele)
- Ureteral triplication/quadruplication are very rare
- Bifid pelvis: seen in 10% patients (normal variant)
Neonatal hydroureteronephrosis
- Start antibiotic prophylaxis (amoxicillin 10-15mg/kg daily), treat for at least 6-12mo
- Obtain postnatal renal US 48hr after birth, bladder images will differentiate ectopic ureter vs megaureter vs ureterocele
- Examine for evidence of ureterocele
- VCUG recommended if bilateral hydroureteronephrosis or bladder/renal anomalies on renal US
- VCUG optional if unilateral hydroureteronephrosis and no bladder/renal anomalies on renal US
- Obtain VCUG to define anatomy prior to any interventions
- Obtain renal scan if ureteral dilation > 10mm, consider foley to optimize drainage
Megaureter
- Can be obstructing, refluxing, both, or neither
- Primary obstructed megaureter (POM): likely due to distal adynamic segment towards UVJ, may present with UTI, pain, or hematuria
- Most nonrefluxing megaureters < 10mm diameter resolve spontaneously with antibiotic prophylaxis along
- Antibiotic prophylaxis: start immediately after diagnosis
- Surgical indications: recurrent UTIs, worsening dilation, differential renal function < 40% or change of > 5% on sequential scans
- Surgical principles: stenotic ureter excised, megaureter straightened/tapered (plication or excisional tapering) with length/diameter ratio 5/1
- Urgent decompression can be performed with nephrostomy tube or cutaneous ureterostomy
- Outcomes: 90% success rates, complications include obstruction, relux, and persistent dilation
- Can consider UVJ balloon dilation with 2-6mo stent
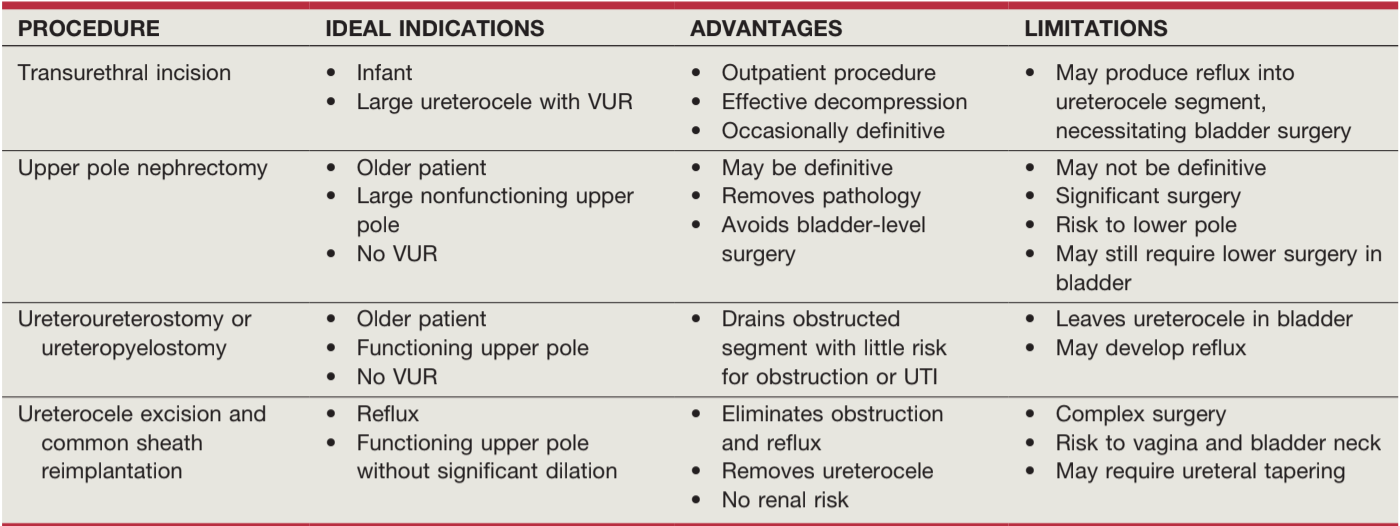
Ureterocele
- Intravesical: entirely within bladder and above bladder neck
- Ectopic: some portion sits permanently at bladder neck or urethra
- Cecoureterocele: orifice is in bladder but ureterocele cavity extends submucosally into urethra
- Can prolapse as an interlabial mass, distinct from vagina
- Urgent management may require transurethral incision or nephrostomy tube
- Transurethral incision (TUI): no difference in technique outcomes, larger holes demonstrate greater reflux risk (0-50%), 78-97% success rates
- Observation: no evidence obstruction or UTI
- Upper pole heminephrectomy: nonfunctional dilated upper pole, no need for ureterectomy
- Common sheath reimplantation: refluxing lower pole and functional upper pole
- Ureteral reimplant: functional upper pole, non-refluxing lower pole
- End ureterostomy can provide temporary relief
Ectopic ureter
- Gender difference: ureter always enters proximal to male urethral sphincter (no incontinence), ectopic ureter may present as incontinence in females due to vaginal insertion
- Acute infection: consider nephrostomy tube or cutaneous ureterostomy
- Surgical management: reimplantation if single, ureteroureterostomy if duplicated, (hemi)nephrectomy if nonfunctional
Zinner syndrome
- Definition: ectopic ureter, seminal vesicle cyst, renal agenesis
- Initial evaluation obtain pelvic US in neonatal period, after puberty onset, or if new LUTS/pain develop
- Voiding symptoms: evaluation with uroflow and PVR, consider urodynamics if abnormal voiding pattern, patients with obstruction may benefit from cyst excision (versus patients with poor emptying)
- a-blockers: offer to patients with LUTS, SV cyst < 5cm
- Infection: manage with antibiotics/drainage, increases risk for infertility
- Surgical intervention: consider if pain, infection, or cyst size ≥ 5cm
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO)
Principles and presentation
- Definition: any restriction to urinary outflow that if left untreated will lead to progressive kidney damage
- Most UPJO in neonates are due to intrinsic narrowing, whereas older children usually caused by lower pole accessory vessel
- VUR can cause secondary UPJO due to ureteral kinking, may improve spontaneously after VUR treatment (staged approach preferred)
- Contralateral UPJO seen in 10-40%
- Ureteral polyp: can cause obstruction and hematuria, seen in 0.5% patients undergoing pyeloplasty, perform ureteroscopic removal
Surgical management
- Indications: increasing hydronephrosis on US, worsening differential renal function, breakthrough infections, or flank pain
- Anderson-Hynes dismembered pyeloplasty: gold standard, spatulate ureter laterally and pelvis medially, excess ureter (usually stenotic portion) excised after reanastomosis
- Nondismembered pyeloplasty: variety of techniques - Foley Y-V plasty, Heineke-Mickulicz, vertical flap, spiral flap
- Ureterocalicostomy: rarely used, indicated for severely scarred ureter or repeat surgery
- Stenting: normally performed to prevent leak, but can be skipped (requires second anesthesia for stent removal), warrants foley for 24-48hr to prevent reflux
- Success rates: 90-100% (symptom resolution, improved hydronephrosis, no need for reoperation)
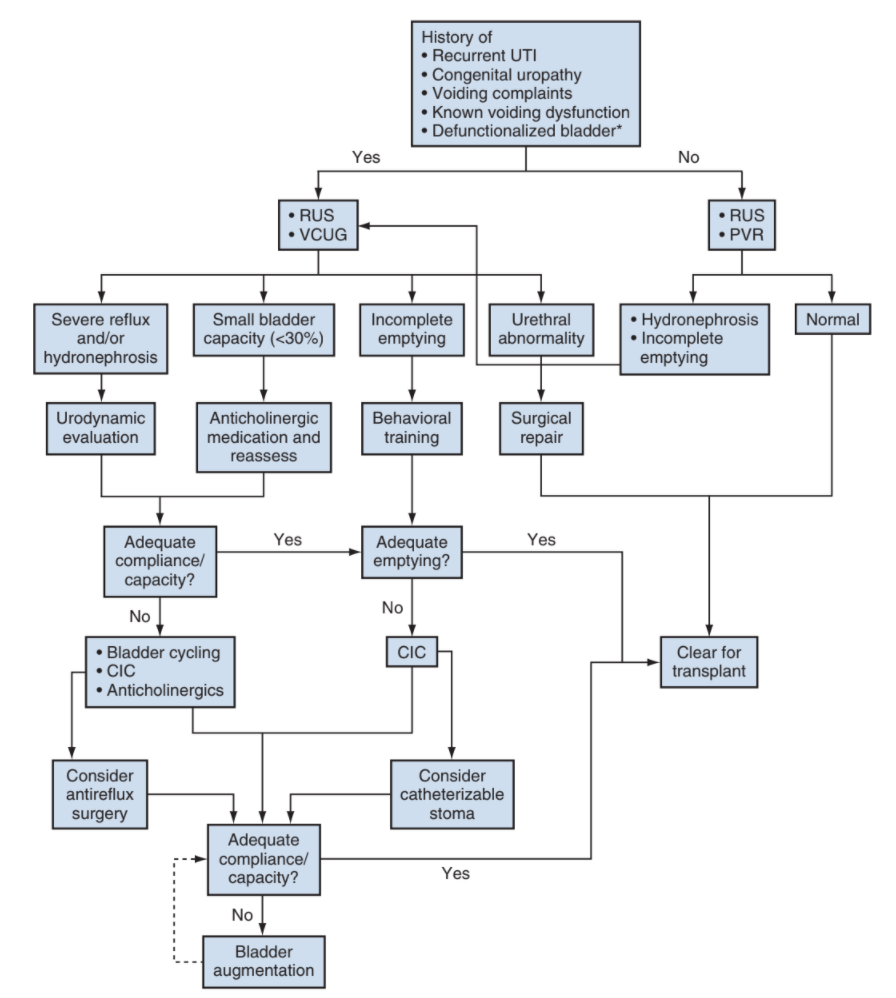
Kidney Transplants
Preparation
- Urodynamics: perform if known NGB, hx PUV, hx ureterocele, severe voiding dysfunction, high grade hydronephrosis, recurrent UTIs
- Most common bladder abnormalities in ESRD: low capacity, hypercontractility, poor compliance
- Bladder augmentation: may be beneficial in contracted bladders (capacity < 75% expected for age) and does not increase transplant complication risk, but must factor in location of pedicle and catheterizable channel so that they do not interfere with transplant
Procedural tips
- Anastomoses: renal vein to vena cava end to side, renal artery to common iliac end to side, ureter to bladder via extravesical approach (or donor to native ureter end to side)
- Indications for pretransplant nephrectomy: poorly controlled HTN, severe nephrotic syndrome, severe polyuria, recurrent upper tract infections, large stone burden, high malignancy risk, large kidneys (make room for transplant), severe reflux
- Stent is not required
Kidney Stones
Considerations
- 50% will have a recurrence within 3-5 years of first episode
- Increased risk for CKD, decreased BMD, and heart disease
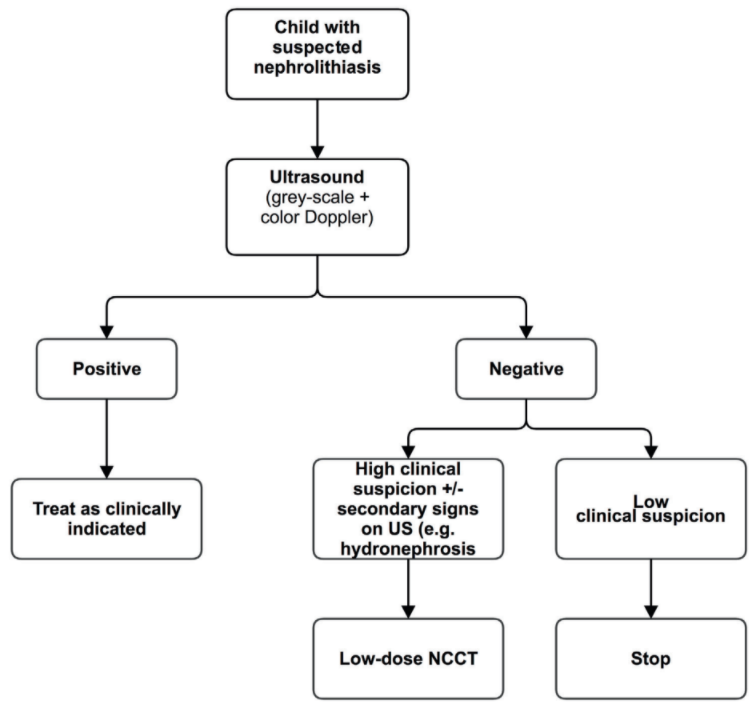
- Obtain CT imaging only if renal US is nondiagnostic and clinical suspicion is high
- US stone criteria: hyperechoic focus in kidney + twinkle artifact (multicolor signal on Doppler) - 70% sensitivity, 95% specificity
- Neonatal nephrocalcinosis: seen in 7-41% preterm infants in NICU, most resolve spontaneously, only 15% will require further interventions
Urine stone workup findings
- Hypercalciuria: 4 mg/kg/day if > 2yo, Ca/Cr ratio > 0.21mg/mg
- Hyperoxaluria: primary may require liver/kidney transplant, secondary caused by increased gut absorption
- Hypocitraturia: Cit/Cr ratio < 128mg/g in boys and < 300mg/g in girls
- Cystinuria: normal excretion < 60 mg/d/1.73m2 BSA
- Hyperuricosuria: leads to epitaxy (uric acid acts as nidus)
Prevention
- Fluids: up to 1.5-2L/m2 for cystinuria
- Sodium: limit to 2-3mEq/kg/d or 2.4g/d in teenagers/adults
- Calcium: maintain normal levels, low Ca may worsen stone risks
- Protein: do not exceed normal requirements
- Oxalate: majority (80%) does not come from diet, but can limit if proven hyperoxaluria
- Protective factors: citrate, potassium, magnesium
Medications
- Alpha blockers: can be given for acute stone episode if < 10mm, overall utility unknown
- Thiazides: hypercalciuria resistant to low sodium diet, 1-2mg/kg/d
- K citrate: low/normal citrate and CaOx stones, 2-4mEq/kg/d
- Thiola: prevent disulfide bridge formation
- Allopurinol: hyperuricemia + hyperuricosuria, 4-10mg/kg/d (max 300mg/d), treat uric acid stones with hydration and alkalinization
- Pyridoxine: primary hypoxaluria Type 1, 2-5mg/kg/d and titrate up
Surgical management
- Up to 60% will require surgery
- Success rates: 70-97% PCNL, 85-88% URS, 80-83% ESWL
- URS: ureteral stones or renal stones < 2cm
- ESWL: renal stones < 1.5cm, increased need for retreatment if longer infundibulum or infundibulopelvic angle > 45 degrees
- PCNL: renal stones > 2cm
- Similar risks to adult stone surgery, may have higher need for pre-stenting due to narrow ureters
Acute and chronic kidney disease
Acute kidney injury (AKI)
- History: fluid intake, voiding history, bowel history, hematuria, flank pain, systemic symptoms, recent medications
- Exam: blood pressure, mental status, edema/turgor, flank pain, abdominal mass, rash
- Adjuncts: CBC, electrolytes (include Ca/Phos), albumin, renal US, UA (and UCx), consider urine electrolytes, consider biopsy
- General management: supportive fluids, balance electrolytes, consider maximal drainage with catheter, stop nephrotoxic medications
- Hyperkalemia management: furosemide (1-2mg/kg IV), sodium bicarbonate (1mEq/kg), kayexelate (0.5-1g/kg PO or 1.5-2g/kg PR), check EKG, can also consider calcium gluconate (100mg/kg IV max 2g)
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- History: voiding habits, bowel habits, UTI, VUR, spina bifida, SLE, vasculitis
- Family history: CKD, cystic disease, dialysis, transplant
- Exam: flank/abdominal mass, suprapubic fullness, lumbosacral abnormalities, genital abnormalities
- Adjuncts: electrolytes (serum/urine), assess for hematuria/proteinuria, albumin, PTH, CBC, renal US, consider biopsy
- Hypertension management: salt restriction (< 2g/d), enalapril (0.1-0.5mg/kg/d PO, dosed BID), amlodipine (0.1-0.5mg/kg/d PO, dosed QD or BID), furosemide (0.5-1mg/kg PO BID)
- Osteodystrophy: restrict phosphorus (< 15mg/g protein daily), sevelamer (400-1600mg/meal), calcitriol (0.25-1.0mcg/kg/d)
- Acidosis: sodium citrate for infants (1-3mEq/kg/d dosed TID), otherwise sodium bicarbonate (1-2mEq/kg/d dosed TID)
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Baskin, Laurence S. Handbook of pediatric urology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018.
- Bearrick, E. N., and D. A. Husmann. "Screening for Zinner syndrome in patients with a congenitally solitary kidney: lessons learned." Journal of Urology 210.6 (2023): 888-898.
- Herndon, C. and R. Zee. "Perinatal Urology." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Olsen, L. and Y. Rawashdeh. "Surgery of the Ureter in Children: Ureteropelvic Junction, Megaureter, and Vesicoureteral Reflux." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Peters, C. and A. Lorenzo. "Urologic Considerations in Pediatric Renal Transplantation." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Pope, J. "Renal Dysgenesis and Cystic Disease of the Kidney." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Stanasel, I. and C. Peters. "Ectopic Ureter, Ureterocele, and Ureteral Anomalies." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Tasian, G. and L. Copelovitch. "Management of Pediatric Kidney Stone Disease." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Vanderbrink, B. and P. Reddy. "Anomalies of the Upper Urinary Tract." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).