Neuromuscular Voiding Dysfunction
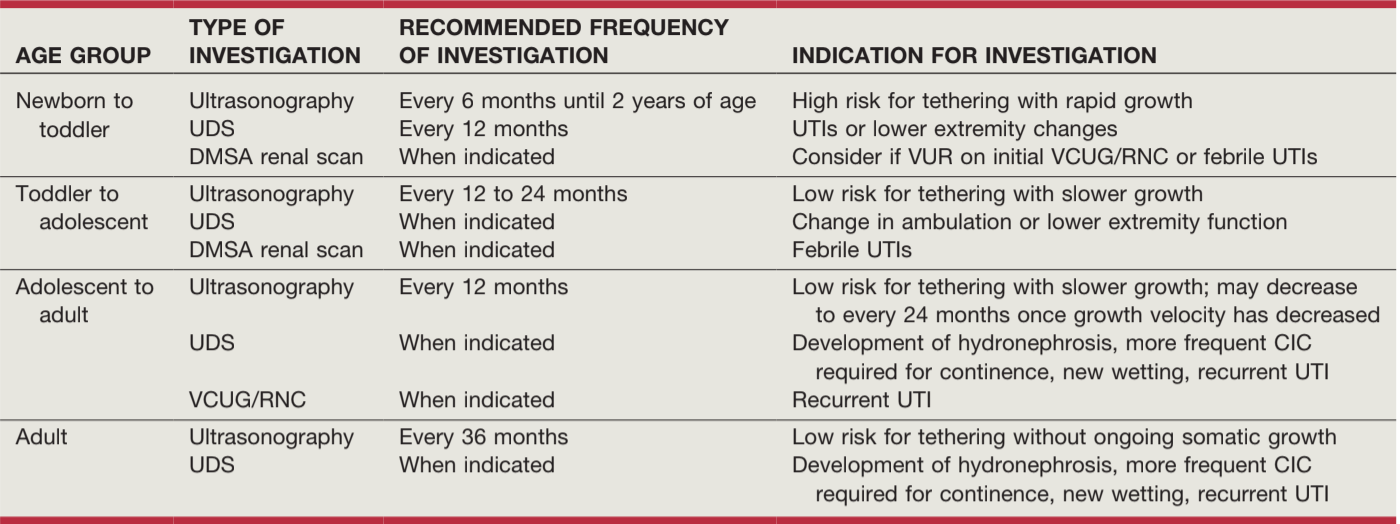
ICCS recommendations for pediatric NGB, from Campbell's

CDC recommendations for spina bifida, from Campbell's
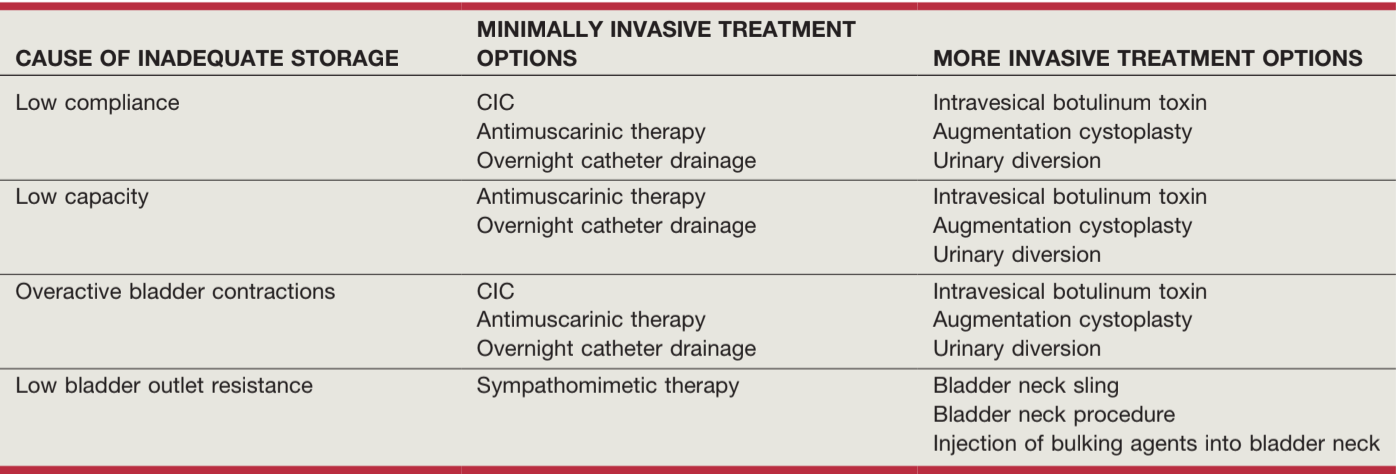
Recommendations for inadequate storage, from Campbell's
Neural tube defects
- Obtain baseline RUS and VCUG as soon after birth as possible, decide whether to start CIC regimen based on results and PVRs
- Pre-UDS CIC: recommended for high residuals (≥ 30mL), trabeculated bladder, high grade reflux (Grade 5), and high grade hydronephrosis (SFU 3-4)
- Perform UDS within 3mo birth (usually after spinal cord closure)
- UDS findings: bladder/sphincter synergy (26%), dyssyngery (37%), or complete denervation (36%)
- Post-UDS CIC: recommended for DLPP > 40, DSD, or Grade 5 VUR, start oxybutynin 0.2mg/kg TID
- VUR: seen in 3-5% newborns, 30-40% by 5yo if untreated, treat with CIC + anticholinergics
- Occult dysraphisms: if not diagnosed by age 3yo, 92% develop UMN or LMN lesion (tethered cord, lipoma compression)
- Crede voiding: avoid, increases reflux and potential for upper tract damage
- Cystatin C: serum levels provide more accurate estimate of GFR
- Bowel function: managed with laxatives, enemas, frequent BMs, and manual stimulation
- Antegrade continence enema (ACE): administered via appendicostomy or cecostomy, 1-2L fluid 4-7x weekly
- Sexual function: 70-92% can obtain erection, 40-75% can ejaculate, 8-83% men and 23-69% women are sexually active, 70-80% able to achieve pregnancy
- Management of Myelomeningocele Study (MOMS): prenatal surgery reduces fetal/neonatal death or CSF shunting (RR 0.7), but 40% still required shunting and pregnancy complications were higher and had higher risk for spinal cord tethering
Other neuromuscular disorders
- Sacral agenesis: MRI confirms acute cutoff of conus at T12, obtain RUS/VCUG, manage based on UDS findings
- Anorectal malformations: GU abnormalities more likely if supralevator (vs infralevator) fistula insertion, often have DO + DSD, obtain RUS, obtain UDS if bony abnormalities, spinal cord defect, or RUS/VCUG abnormalities
- Post-pelvic surgery: due to splanchnic/hypogastric nerve damage, preop/postop UDS recommended if high risk for injury during surgery
- Cerebral palsy: 16-94% have GU symptoms, mainly incontinence, upper tract injury is rare, manage based on individual picture
- Spinal cord injury: acontractile bladder in acute setting, then may develop DO + DSD, minimal regain of function if cauda equina injured, protect upper tracts
- Transverse myelitis: urinary retention common in acute setting, then develops into DO + DSD, 57-73% require CIC
Management Options
- Goals (in order of priority): protect upper tracts, maintain continence, maintain independence, avoid reconstructive surgery
- Surgical management categories: increase bladder size/compliance, increase bladder outlet resistance, create catheterizable channel
- Most concerning finding is filling pressures > 40, increases risk for upper tract injury
- Anticholinergics: improves capacity/compliance, decreases incontinence and catheterization episodes, side effects (dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, dizziness, headaches) can lead to decreased compliance, no evidence cognitive impairment in children
- Sympathomimetics: improve urethral resistance, but may cause dizziness, nausea, insomnia, headache, retention
- Botox: 65-87% dryness after failing medical management + CIC, 360U max dose
- Augmentation: for poorly compliant small capacity bladders, 0-29% require continued anticholinergics, 15% develop major complications (SBO, transfusions, perforation, UTI/pyelo), cystography diagnostic for augment perforation, 0.6% cancer risk
- Vesicostomy: used for severe reflux despite CIC, CIC non-compliance, poor augment candidates, complications include prolapse, stenosis, bladder stones
- Artificial urinary sphincter: improves outlet obstruction, continence 63-86%, cuff erosion 16-20%, worse bladder function 4-30%, device lifespan 4.6-12.7yrs
- Bladder slings (fascial and synthetic): improves outlet obstruction, continence 30-93%, new detrusor overactivity 33%
- Bladder neck reconstruction (Young-Dees-Leadbetter): excise and tighten bladder neck to maintain continence
- Catheterizable channels (Mitrofanoff, Yang-Monti): use appendix or intestine to create a continent reservoir to make CIC easier
References
- AUA Core Curriculum`
- Austin, P. and A. Seth. "Functional Disorders of the Lower Urinary Tract in Children." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Baskin, Laurence S. Handbook of pediatric urology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2018.
- Estrada, C. and S. Bauer. "Neuromuscular Dysfunction of the Lower Urinary Tract in Children." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Thomas, J., D. Clayton, and M. Adams. "Lower Urinary Tract Reconstruction in Children." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Wilcox, D. and K. Rove. "Clinical and Urodynamic Evaluation of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Children." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).