Kidney Cancer Diagnosis/Workup
RCC Tables
Types of RCC
| Tumor Type | % all RCC | Cellular origin | Nuggets (mainly prognosis) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear cell | 70-80% | Proximal tubule | Aggressive behavior Responds to targeted therapy |
| Papillary Type I | 5-10% | Good prognosis | |
| Papillary Type II | Worse prognosis than Type I | ||
| Chromophobe | 3-5% | Intercalated cells of collecting duct | Sarcomatoid has worse prognosis |
| Clear cell papillary | 5% | Good prognosis with indolent behavior Seen in VHL and ESRD |
|
| Collecting duct (Bellini) | < 1% | Collecting duct | Poor prognosis May respond to chemo |
| Renal medullary | Collecting duct | Poor prognosis Usually seen in sickle cell patients |
|
| HLRCC-associated | - | Early metastasis Poor prognosis |
|
| SDH-associated | Occur in young adults | ||
| MiT Family (Xp11 and t(6;11) | 40% pediatric RCC | ||
| Acquired cystic-disease-associated | Seen in ESRD and ACD patients Good prognosis |
||
| Multilocular cystic clear cell | Mass with multiple cysts Almost uniformly benign |
||
| Tubulocystic | Favorable prognosis | ||
| Mucinous tubular and spindle cell | Favorable prognosis | ||
| Hybrid oncocytic chromophobe | Generally good prognosis Seen in Birt-Hogg-Dube |
||
| Sarcomatoid differentiation | 1-5% | Variant seen in most RCC | Indicates worse prognosis |
| Sarcomatoid differentiation | |||
| Unclassifed | 1-5% | Unclear | Poor prognosis Aggressive behavior |
Familial RCC Syndromes
| Syndrome | Gene/Chromosome | Type of RCC | Associated Findings | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Von-Hippel Lindau (VHL) | VHL (3p25) | Clear cell (may be multifocal) | Renal cysts Hemangioblastomas Retinal angiomas Pheochromocytoma Epididymal cystadenomas |
If < 3cm - active surveillance If > 3cm - nephron sparing surgery |
| Hereditary Papillary Renal Carcinoma | MET (7q31) | Type I Papillary (multiple, bilateral) | None | |
| Birt Hogg Dube (BHR) | FLCN (17p11) | Chromophobe | Oncocytoma Renal cysts Cutaneous fibrofolliculomas Lung cysts Spontaneous pneumothorax |
|
| Cowden Syndrome | PTEN (10q23) | Clear cell Chromophobe Type I papillary |
Mucocutaneous lesions Facial trichilemmomas Breast tumors Epithelial thyroid cancer |
|
| Hereditary Leiomyomatosis RCC (HLRCC) | FH (1q42-43) | Type II Papillary Collecting Duct |
Cutaneous leiomyomas Uterine leiomyomas |
Surgical excision with wide margins |
| Succinate dehydrogenase deficiency RCC | SDHB (qp36) SDHC (1q23) SDHD (11q23) |
Clear cell Chromophobe Type II papillary |
Oncocytoma Paragangliomas Papillary thyroid cancer |
|
| Tuberous Sclerosis | TSC1 (9q34) TSC2 (16p13) |
Clear cell | Angiomyolipoma Oncocytoma Polycystic kidneys Cardiac rhabdomyomas Cutaneous angiofibromas Lymphangiomyomatosis Seizures Autism |
AML: surveillance (< 3cm), everolimus (3-5cm), surgery/embolization (> 5cm) RCC: surgery (> 3cm) |
Diagnosis
Presentation
- Classic triad: flank pain + renal mass + hematuria, seen in < 5% patients - > 60% RCC diagnosed incidentally
- Paraneoplastic syndromes: hypercalcemia, hypertension, polycythemia, anemia, weight loss, fever
- Stauffer syndrome: non-metastatic hepatic dysfunction (3-20% prevalence), normalizes in 60-70% cases after nephrectomy
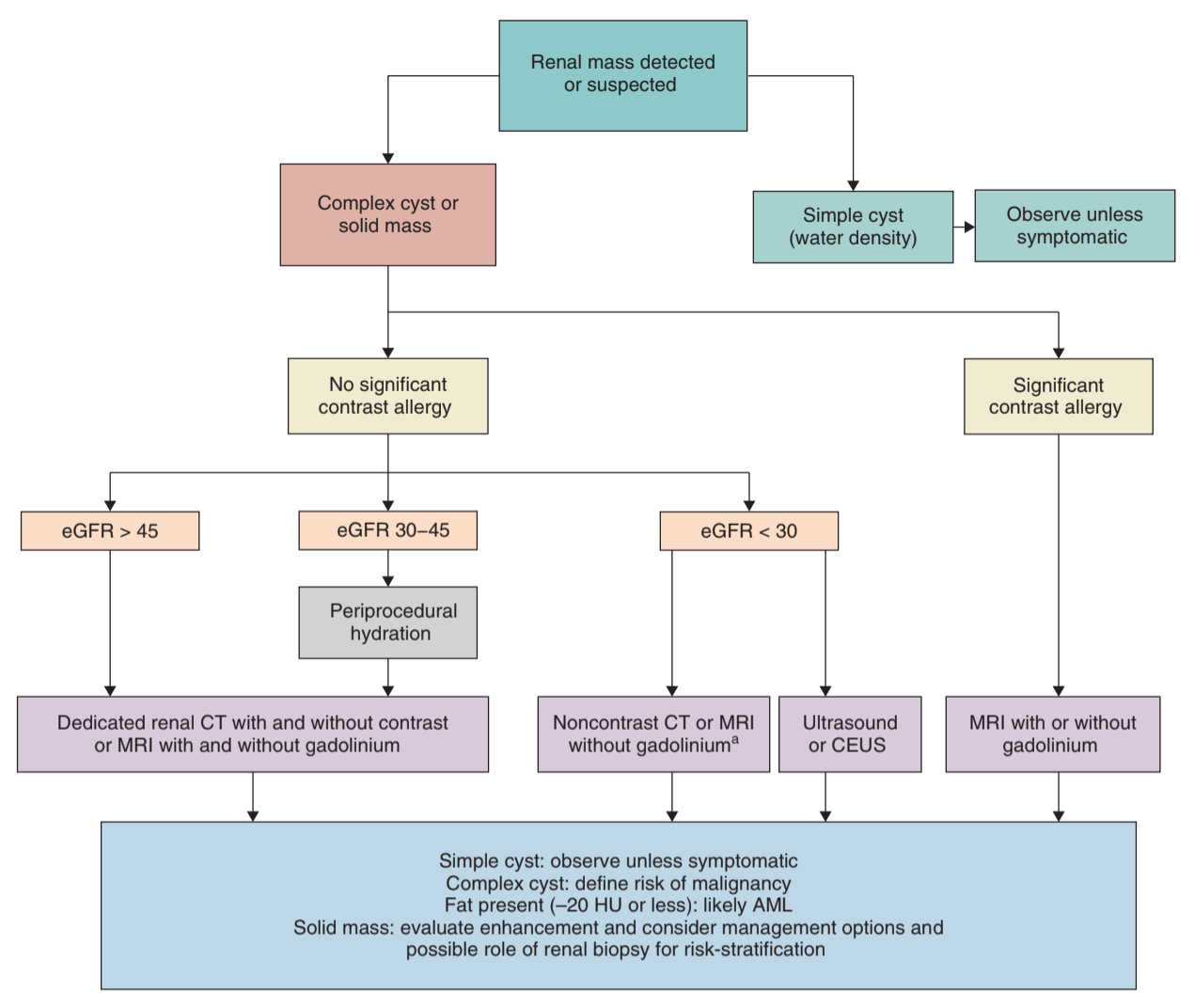
Initial Imaging
- Options: CT/MR w/ + w/o contrast to assess enhancement, consider contrast-enhanced US if unable to undergo CT/MR
- Enhancement: > 15-20 HU with CT, > 20% with MR
- No fat density: intralesion fat likely angiomyolipoma
- Perirenal hematoma: may have underlying malignancy in > 50% cases, reimage in 2-3 months to assess after resolution
- Complexity profiles: RENAL nephometry score, PADUA score, C-index - useful for predicting complexity of surgical resection
Complete the Workup
- Labs: obtain baseline CMP (assess baseline GFR), CBC, UA (assess proteinuria)
- Chest imaging: obtain CXR, or CT chest (if pulmonary symptoms or abnormal CXR)
- Genetics evaluation: recommended if ≤ 45yo, bilateral masses, multifocal masses, personal or family (first/second degree relative) history of renal mass syndrome (even if no one has had renal masses)
- MR indications (after CT): locally advanced disease, equivocal vein involvement, or contrast allergies
- IVC thrombus: MR is best (chest + abdomen), CT may be equivalent, TEE can be considered
- Brain imaging: only if neurologic symptoms, IVC thrombus, or metastatic disease
- Bone scan: only if bone pain or elevaed alkaline phosphatase
- Nephrology referral: GFR < 45, diabetic w/ CKD, proteinuria, or anticipated GFR < 30 after treatment
When to Biopsy
- Accuracy: sensitivity 97.5%, specificity 96.2%, PPV 99.8%, NPV 63% (20-37% missed cancer diagnosis), biopsy nondiagnostic rate 14% (will find cancer on repeat biopsy), perform core biopsy (not fine-needle aspiration)
- Indications: renal mass is thought to be metastatic, inflammatory, infectious, or hematologic
- Young/healthy: no need for biopsy if patient opts for surgery, but can consider if patient wants observation
- Old/frail: no need for biopsy if planning on observing
- Metastatic sites: preferentially biopsy metastatic lesion, consider renal biopsy if considering palliative/cytoreductive nephrectomy
- Biopsy risks: hematoma (5%), significant pain (1%), hematuria (1%), pneumothorax (0.6%), transfusion (0.4%), tumor seeding rare (no reported cases in modern literature with modern biopsy techniques)
Non-RCC Tumors
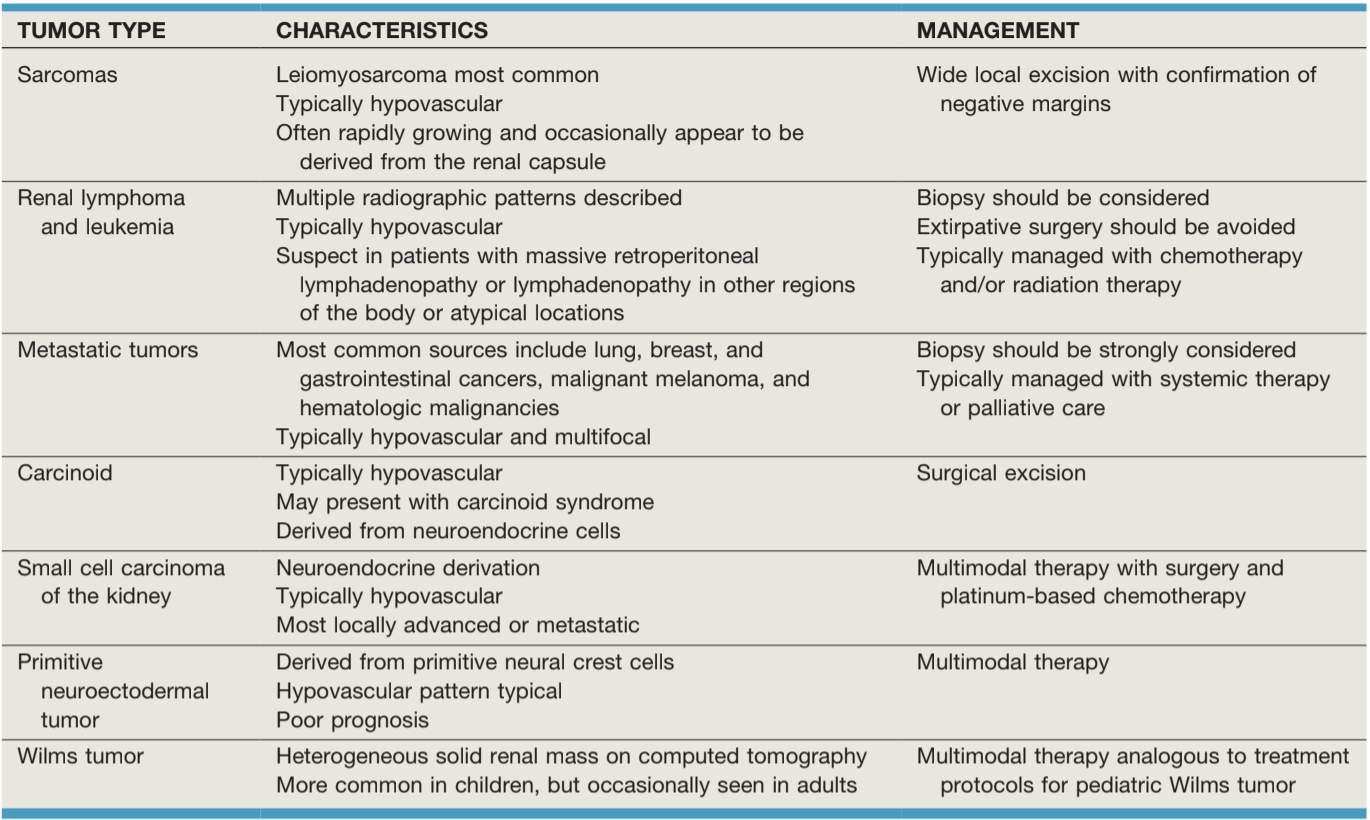
Sarcoma
- 1-2% all renal malignancies
- Do not obey normal tissue planes, may require en bloc resection
- Neoadjuvant XRT may reduce risk of positive margins
Leukemia/Lymphoma
- Rarely presents as primary renal lesion
- Imaging findings: retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy, multiple distinct renal masses, spenomegaly, lymphadenopathy in other areas of the body
- Obtain biopsy to confirm diangosis
- Treat with chemo (R-CHOP) +/- XRT, not surgery
Metastatic disease
- 12% cancer patients have renal metastases
- Most common primaries: leukemia/lymphoma, lung, breast, stomach, colon, cervix, melanoma
- Biopsy indicated if unclear whether primary RCC or metastatic lesion
- Nephrectomy rarely indicated
Benign renal tumors
Renal Cysts
- Seen in up to 10% population
- Indications for intervention: pain, infection, HTN, hemorrhage, rupture
- Management: aspiration, decortication, resection, sclerotherapy, embolization, nephrectomy (partial/radical)
Bosniak Renal Cyst Classification
| Bosniak Class | Findings | % Malignancy | Plan |
| I | Water density Homogenous wall No septa, calcifications, or enhancement |
0-2% | No follow-up required |
| II | Few septations with possible enhancement Fine calcifications No obvious enhancement |
0-18% | No follow-up |
| IIF | Multiple septations Perceived wall/septal enhancmenets Calcifications without enhancement No obvious enhancement |
3-18% | Repeat imaging to assess stability |
| III | Thickened/irregular walls/septations with measurable enhancement | 33-50% | Observation, excision, ablation |
| IV | Complex cystic mass Enhancing nodular components "clearly malignant" |
75-93% | Surgery |
Oncocytoma
- Most common benign renal mass (up to 25% masses < 3cm)
- Can occasionally present with perirenal fat and renal vein invasion
- Association with RCC: ~10% contain RCC, impossible to distinguish on imaging from RCC
- Imaging: may show hypervascularity, central scar, but non-definitive
- Renal biopsy: PPV only 67%, not recommended
- Differential: compare histology for chromophobe RCC, CK7 rarely positive in oncocytoma
- Management: can consider observation, growth rate slower than for chromophobe RCC (average 0.14mm/yr vs 0.38mm/yr)
Angiomyolipoma
- Composed of dysmorphic blood vessels, smooth muscle, and adipose tissue
- More common with tuberous sclerosus or lymphangiomyomatosis
- Wunderlich syndrome: spontaneous retroperitoneal hemorrhage, seen in 15% AMLs
- Diagnose with presence of macroscopic fat (HU -15-20) on CT/MR
- Fat-poor AML: seen in 4-14%, difficult to differentiate from RCC
- MR imaging: recommended in women < 55yo to confirm/rule out AML
- Management: observation if < 4cm and asymptomatic, embolization for active hemorrhage or > 4cm, surgery as last resort (but less surveillance required), consider everolimus if TS
Other masses
- Papillary adenoma: small (< 0.5cm) usually incidentally found in nephrectomy specimens, possible precursor to papillary RCC
- Metanephric adenoma: possibly mature form of Wilms tumor, enhance less than normal renal parenchyma, diagnosis usually confirmed after resection
- Cystic nephroma: appears similar to Wilms tumor, no blastemal/embryonal components
- Mixed epithelial/stromal tumor: associated with estrogen replacement, present as cystic mass
- Leiomyoma: appear similar to chromophobe RCC, usually hyperdense and homogenous enhancement
- Hemangioma: associated with Klippel-Trenaunay and Struge-Weber
- Lymphangioma: abnormal lymphatics create dilated cystic masses, may present with obstruction, HTN, hematuria, and cyluria, can treat with aspiration, sclerosis, excision
- Juxtaglomerular cell tumor (reninoma): presents with hyperaldosteronism, rare cause of HTN, treat w/ partial nephrectomy, 10% have persistent HTN after resection
- Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor: very small (< 5mm) usually incidentally diagnosed
Pseudotumors
- Examples: hypertrophied column of Bertin, fetal lobation, dromedary hump, hilar lip/uncus, nodular compensatory hypertrophy
- Imaging: CT renal mass protocol, DMSA renal scan (normal uptake)
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Campbell, C., B. Lane, and P. Pierorazio. "Malignant Renal Tumors." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Campbell, Steven C., et al. "Renal mass and localized renal cancer: evaluation, management, and follow-up: AUA guideline." The Journal of Urology (2021)
- Parker, W. and M. Gettman. "Benign Renal Tumors." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Tracy, C. and J. Cadeddu. "Nonsurgical Focal Therapy for Renal Tumors." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.