Conservative Management of Voiding Dysfunction
Lifestyle changes
- Weight loss: 8kg loss results in average 58% reduction in SUI
- Fluid management: maintain 1.5L minimum intake, minimize fluids before bed, alter diuretic timing, minimize caffeine intake
- Bowel management: encourage regular BMs and fiber intake, constipation worsens OAB symptoms
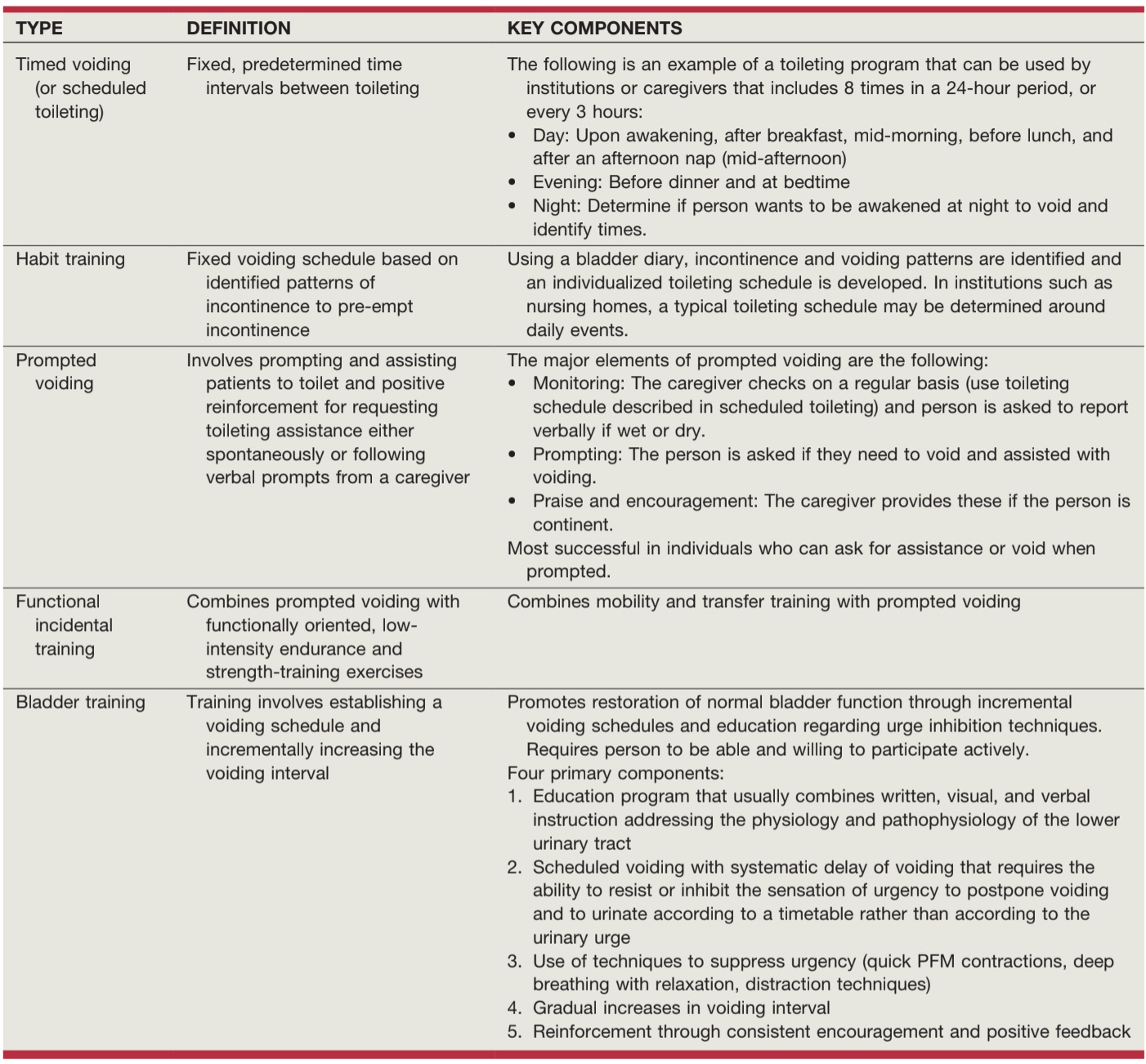
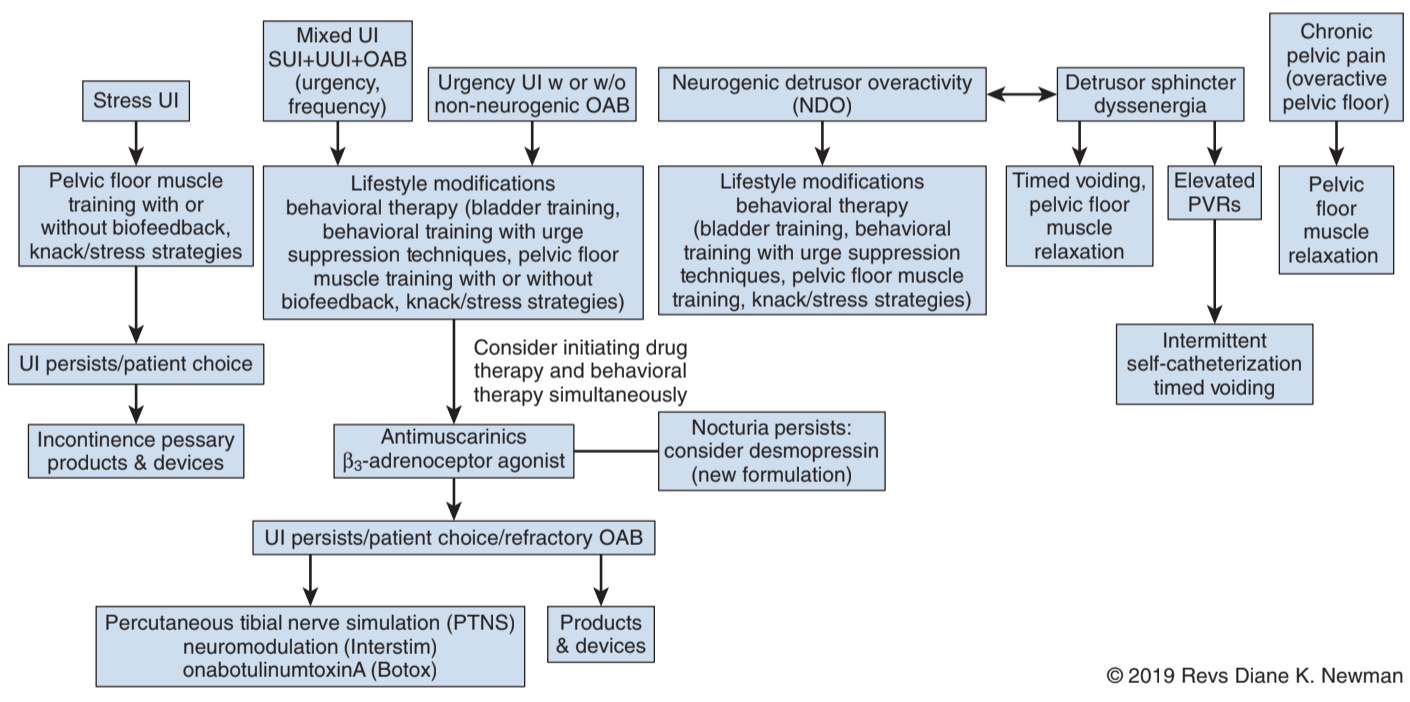
- Behavioral training: works on urge suppression, timed voiding
Pelvic floor interventions
- Physical therapy: improvements as long as exercises are continued, work on both relaxation and contraction
- Biofeedback: allows patients to monitor symptoms and responses in real time to understand how to modify and improve their responses, can also use electrostimulation
- Vaginal weights: contract pelvic floor to keep weight inside vagina, use for 10-15min BID
Anti-incontinence devices (pessary)
- Placed transvaginally, variety of shapes/sizes, prevents prolapse and SUI
- Common side effects: discharge, odor
- Rare side effects: vesicovaginal fistula, rectovaginal fistua, erosion, impaction, bleeding
- Contraindications: active infection, severe ulceration, silicone/latex allergy, noncompliance with follow up
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Newman, D. and K. Burgio. "Conservative Management of Urinary Incontinence." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.