Recurrent UTIs
Workup and Diagnosis
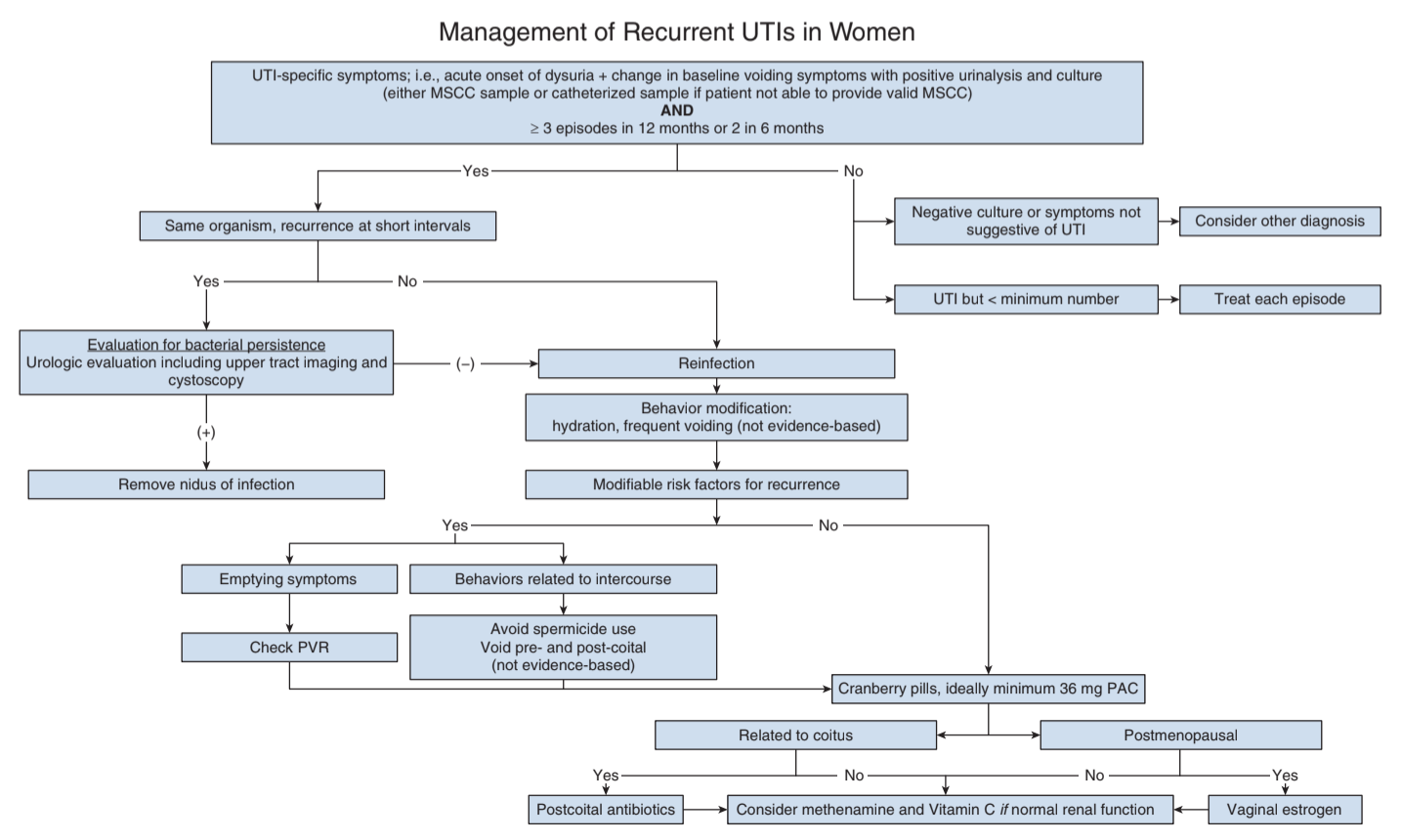
Definitions
- Recurrent UTI: 2+ UTIs in 6mo or 3+ UTIs in 1yr
- Uncomplicated UTI: UTI without anatomic/functional abnormalities that would increase risk of developing UTI
- Complicated UTI: UTI in setting of anatomic/functional abnormalities, immunocompromised, or MDRO
- "Index" patient: otherwise healthy adult woman w/ uncomplicated UTI, excluding pregnancy, immunocompromixed, anatomic/functional abnormalities, catheters, bacteremia, neurologic disease, post-GU procedures
History
- UTI symptoms: dysuria, frequency, urgency, nocturia, incontinence, hematuria, pneumaturia, fecaluria
- Baseline voiding symptoms: # voids, urgency, straining, incomplete emptying, pelvic pressure, vaginal bulge, dysuria, dyspareunia, GU/pelvic pain
- Bowel symptoms: diarrhea, constipation, fecal incontinence
- Other symptoms: back/flank pain, vaginal discharge/irritation
- UTI hx: frequency, positive cultures, type of bacteria
- Antibiotics: prior usage, complications, allergies
- GU hx: catheter usage, prior GU/pelvic surgery
- GYN hx: menopause status, contraceptive usage, spermicides, E/P products
- Sexual hx: # partners, new partners within past year, post-coital UTIs
- Other hx: travel history, family history of UTI (in 1st degree relative)
- Risk factors for complex UTI: pregnancy, immunocompromised, anatomic/functional abnormalities, neurologic disease
Exam
- Pelvic organ prolapse
- Urethra/bladder: tenderness, diverticulum, cysts, incontinence
- Vaginal mucosa: atrophy, irritation
- Pelvic floor: tone, tenderness, trigger points
- Neuro exam
Adjuncts
- Post-void residual: no threshold for (ab)normal value, confirms patient able to adequately empty
- Confirm diagnosis with positive urine culture
- Persistent negative UCx: pursue workup for OAB, cancer, stones, pelvic floor dysfunction, interstitial cystitis
- Cystoscopy and upper tract imaging: not required in an index (uncomplicated) patient, only find abnormalities in 2-6% of patients (and usually suspected based on history/physical)
Indications for cystoscopy and imaging
- Consider if patient does not respond to adequate UTI treatment or high suspicion, helps to assess anatomic/functional abnormalities that increase risk for UTI
- Imaging choice: renal/bladder US should be first choice, only consider CT if high concern or abnormal findings on US
- VCUG: obtain if VUR is suspected
- MRI: obtain if concern for urethral diverticulum
Management
Antibiotic therapy options
- Self-start therapy: indicated for a reliable patient who will provide UCx and immediately starts taking abx
- Post-coital abx: prescribe if clear pattern related to coitus
- Prophylactic abx: recommended for 6-12mo duration, but risk of abx resistance
Vaginal estrogen
- Benefits: peri/post-menopausal women without obvious contraindications, can help if UTI during breastfeeding, minimal systemic absorption, minimal risk of cancer or thromboembolic events
- 17b-estradiol cream: 2g daily x2 weeks, then 1g 2-3x per week
- Equine estrogen cream: 0.5g daily x2 weeks, then 0.5g 2x per week
- Vaginal tablet (estradiol hemihydrate): 10mcg daily x2 weeks, then 10mcg 2-3x per week
- Vaginal ring (17b): 2mg ring releases 7.5mcg daily for 3mo
Non-abx proven therapies
- Cranberry: proanthocyanidins prevent bacterial adhesion to urothelium, lower rUTI (RR=0.67), tablets are better than juice (sugar), take BID, take 36mg-72mg PAC equivalents
- Increased water intake: benefit if baseline UOP < 1.5L
- Timed voiding: warranted if hx holding urine for long periods
Non-abx less proven therapies
- Methenamine: converted to formaldehyde in urine, take 1g BID, take with 1-4g ascorbic acid (acidified urine increases effects), do not take if CrCl < 50, no benefit if catheter present (needs time to dwell in bladder)
- D-mannose: reportedly reduces rUTI, proper dosing not known
- Doesn't work: post-coital urination, douching, pubic shaving, avoiding thong underwear, oral estrogen, lactobacillus
Antibiotic options
| Culture-proven UTI treatment | TMP/SMX DS BID x3 days Nitrofurantoin 100mg BID x5 days Fosfomycin 3g single dose Second line options: beta-lactams, fluoroquinolones |
|---|---|
| Daily prophylaxis | TMP 100mg QD TMP/SMX SS QD or SS 3x/week Nitrofurantoin 50mg or 100mg QD Cephalexin125mg or 250mg QD Fosfomycin 3g q10d |
| Post-coital dose | TMP/SMX SS or DS Nitrofurantoin 50mg or 100mg Cephalexin 250mg |
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Anger, Jennifer, et al. "Recurrent Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections in Women: AUA/CUA/SUFU Guideline." The Journal of urology (2022).
- Cooper, K. L., G. M. Badalato, and M. P. Rutman. "Infections of the urinary tract." Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Elsevier (2020): 1129-1201.
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.