Autoimmune-related dermatologic diseases

Allergic dermatitis, from Campbell's
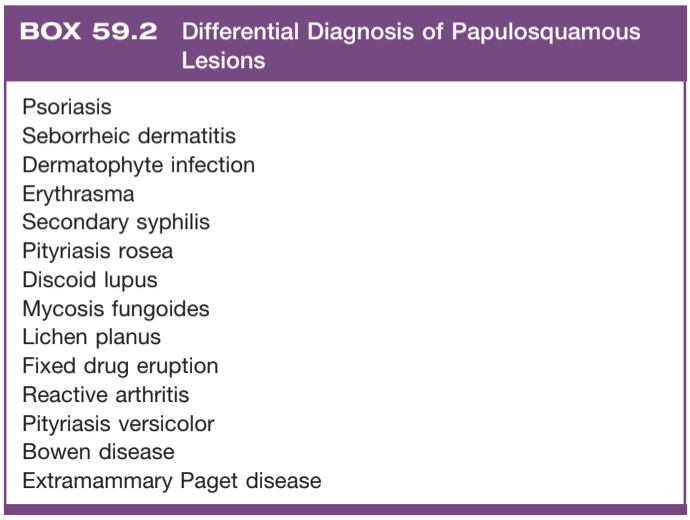
Papulosquamous disease, from Campbell's

Vesicobullous disease, from Campbell's

Ulcers, from Campbell's
Allergic dermatitis
- Eczema: causes intense itching, usually with extragenital manifestations, associated with environmental triggers, treat topically with nonalkali soaps and emollients, orally with steroids, antihistamines
- Contact dermatitis: avoid exposure to irritants, may be caused by genital piercing, ask about products used on genitals
- Erythema multiforme: red papules that evolve into target lesions, most often seen with herpes infection
Drug-related reactions
- Fixed drug reaction: well-defined bullous lesions that have hyperpigmentation after resolution, repeat exposure causes reaction in same location, most commonly due to penicillins, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, salicylates, barbituates
- Coumarin necrosis: rare, usually seen with protein C deficiency, painful lesions that progress to hemorrhagic necrosis and priapism, manage with heparin and Vitamin K, usually only seen with doses above 10mg
- Stevens Johnson syndrome: develop macules and blisters similar to severe burns, usually drug related, treat with systemic therapy, usually safe to place catheter and no need for cystoscopy
Papulosquamous disorders
- Psoriasis: sharply demarcated erythematous plaque with silvery scales, treat with short course topic steroids, do not treat genital lesions with UV therapy
- Reactive arthritis: urethritis + arthritis + ocular findings + oral ulcers, occurs after STI or GI infection, more common in HIV+ patients, may have psoriaform penile lesions (balanitis circinata), treat with topical steroids
- Lichen planus: purple papules/plaques sometimes with ulceration, 2/3 spontaneously resolve within 1yr, treat with topical steroids
- Lichen nitidus: fleshy papules in clusters, most spontaneously resolve, treat with topical steroids
- Lichen sclerosus: tissue pallor and scarring, can cause phimosis and urethral strictures in men, can cause vulvar adhesions and vaginal obstruction in women, treat with topical steroids (clobetasol 0.05% BID), consider daily catheterization using steroid cream as lubricant for intraurethral manifestation, may require circumcision
- Seborrheic dermatitis: pigmented plaques with adherent scale, more common in uncircumcised patients, severe manifestations seen in underlying HIV, treated with topical antifungals (unclear if fungal origin)
Bullous diseases
- Pemphigus vulgaris: 50% have genital lesions, painful oral lesinos are characteristic, treat with systemic steroids
- Bullous pemphigoid: itching that becomes blisters, less common mucosal involvement than vulgaris, treat with systemic steroids
- Dermatitis herpetiformis: cutaneous manifestation of celiac disease, avoid gluten, may treat with dapsone
- Hailey-Hailey disease (benign familial pemphigus): rare, caused by abnormal cell adhesion, intertriginous itching, pain, and foul odor, avoid friction/sweating, treat with steroids
Ulcerative diseases
- Aphthous ulcers: usually seen in mouth (canker sores) but can appear on genitals, if seen together with uveitis consider Behcet disease, variety of severity in presentation
- Pyoderma gangrenosum: ulcers with purulent base, wide variety of underlying causes, genital involvement uncommon
References
- Link, R. and N. Tang. "Cutaneous Diseases of the External Genitalia." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).