Hematuria Evaluation
Assessing hematuria risks
Epidemiology
- AUA definition: 3+ RBCs on microscopic UA warrant assessment and potential hematuria workup, single urinalysis with RBCs is all that is required for a hematuria workup, dipstick alone is not adequate for diagnosis
- Prevalence: 6.5% healthy patients have microscopic hematuria on screening tests
- Malignancy prevalence: 1-3.1% w/ microscopic hematuria, 13.2% w/ gross hematuria
- Unknown cause: 33-67% patients do not have diagnosible cause of hematuria (positional, physical activity, recent intercourse)
Risk factors
- Smoking: increases risk of bladder cancer
- Radiation: XRT cystitis, secondary malignancy, fistula
- Chemotherapy: cyclophosphamide can lead to hemorrhagic cystitis
- UTI: hematuria may be a presenting symptom
- Chronic catheter: irritation or development of SCC bladder cancer
- Chemical exposure: benzenes, aromatic amines increases risk of bladder cancer
- Hx stones, BPH, trauma: benign causes of hematuria
- Dysuria: in absence of UTI, may be presenting symptom of carcinoma in situ
- Hx cancer: either GU-specific or syndromic (Lynch, VHL)
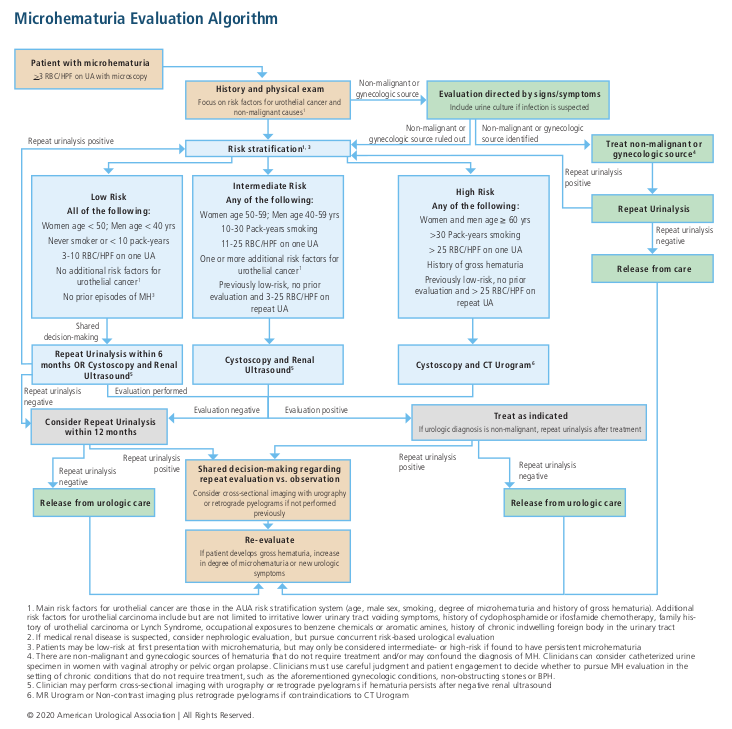
Hematuria workup
Risk Groups
| Risk | Needs all criteria? | Gender/Age | Smoking (packyears) |
# RBC (UA x1) |
Urothelial cancer risk factors* |
Prior hematuria | Probability malignant cause | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Yes | Women < 60 Men < 40 |
< 10 | 3-10 | None | No | 0.2-0.5% | Repeat UA in 6mo |
| Intermediate | No | Women > 60 Men 40-59 |
10-30 | 11-25 | 1+ | Persistent 3-25 RBC | 1.3-1.6% | Cysto + RBUS Can offer cytology/urine tumor markers |
| High | Men 60+ | > 30 | > 25 | 1+ (needs another high risk feature) | Gross | 10.8-11.1% | Cysto + CTU |
*Risk factors include irritative voiding symptoms, prior pelvic radiation, prior cyclophosphamide, history urothelial cancer or Lynch syndrome, prior occupational exposures, and chronic indwelling foreign body
Considerations
- UTI: hematuria in setting of UTI does not warrant workup, perform workup if hematuria persists after treatment (wait 3wks-3mo)
- Anticoagulation: patients on anticoagulation should undergo same workup
- If benign cause identified and treatment, discuss with patient whether further workup is warranted
- Nephrologic cause suspected: perform full workup, increased risk for GU cancers in setting of decreased renal function
- Family history: if history of RCC, genetic renal tumor syndrome, Lynch syndrome, patients should undergo cross-sectional imaging regardless of other risk factors
Workup components
- Upper tract imaging: CTU, MRU, renal US + retrograde pyelograms
- Renal US: less sensitive for upper tract urothelial cancer but very sensitive for renal neoplasms, recommended option for intermediate risk patients
- Cystoscopy: perform without enhancement (blue light), preferable as screening test
- If persistent/worsening hematuria after renal US, obtain cross-sectional imaging
- Cytology/tumor markers: do not use for low or high risk patients (except if equivocal workup and persistent hematuria/irritative symptoms), do not obtain after otherwise normal cystoscopy, can use for intermediate risk patients instead of cystoscopy (but proceed with cystoscopy if repeat UA shows hematuria 12mo after initial evaluation)
Follow-up
- Probability of subsequent cancer: less than 1% if negative initial workup, equivalent to general population risk for developing GU cancer
- Negative workup: consider annual microscopic UA
- Worsening hematuria or urologic symptoms: obtain further workup
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Barocas DA, Lotan Y, Matulewicz RS, Raman JD, Westerman ME, Kirkby E, Pak L, Souter L. Updates to Microhematuria: AUA/SUFU Guideline (2025). J Urol. 0(0). doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000004490.
- Boorjian, et al. "Evaluation and management of hematuria." Campbell-Walsh Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier (2020): 247-259.
- Castle, E., C. Wolter, and M. Woods. "Evaluation of the Urologic Patient: Testing and Imaging." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Lee, Joo Yong, et al. "Hematuria grading scale: a new tool for gross hematuria." Urology 82.2 (2013): 284-289.
- Lisanti, Christopher J., et al. "What is the relative risk of urologic malignancy in microscopic hematuria patients after negative evaluation? A long-term population-based retrospective analysis of 8465 patients." Abdominal Radiology 48.3 (2023): 1011-1019.
- Stout, Thomas E., Michael Borofsky, and Ayman Soubra. "A visual scale for improving communication when describing gross hematuria." Urology 148 (2021): 32-36.
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.