Management of Gross Hematuria and Hemorrhagic Cystitis
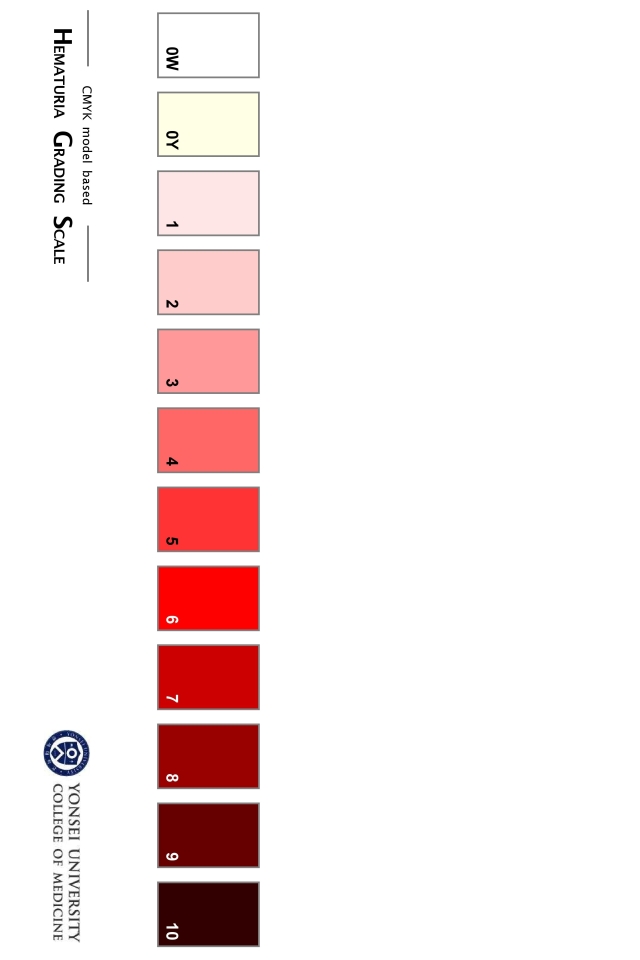
Hematuria grading scale Option #1, from Lee 2013
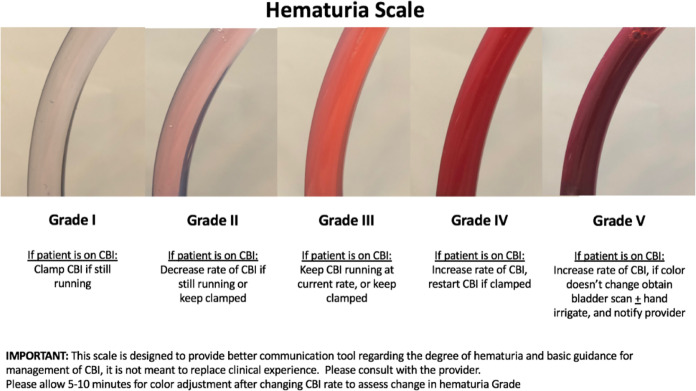
Hematuria grading scale Option #2, from Stout 2021
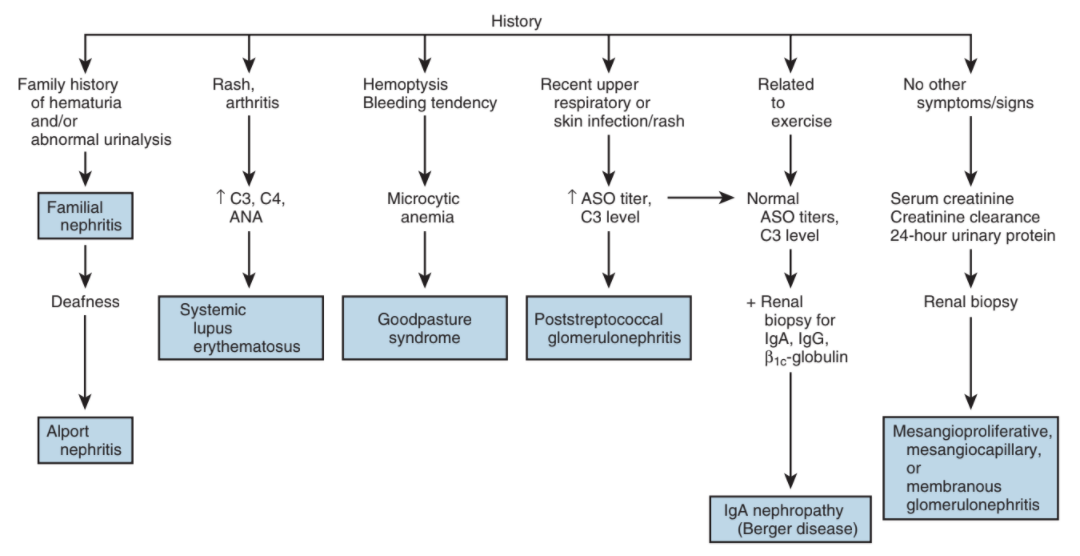
Glomerular causes of hematuria, from Campbell's
Hematuria management
Initial Evaluation of Gross Hematuria
- Safe to discharge: able to empty bladder (check bladder scan), no blood clots (check urine appearance), not actively bleeding (stable Hgb, non-hypotensive)
- Retention with mild bleeding: likely prostatic origin, attempt regular catheter placement (often results in clear yellow urine, catheter bypasses prostatic bleeding)
- Retention likely secondary to clot burden: likely prior XRT or surgery, place large 3-way Rusch catheter, manually irrigate, start continuous bladder irrigation (CBI)
- Persistent bleeding despite CBI: consider traction, OR clot evacuation, other cause-specific treatments
BPH
- Cause: increased vascularity in hyperplastic tissue secondary to VEGF
- Finasteride: inhibits androgen-stimulated angiogenesis and decreases VEGF expression, 90% symptom improvement, decreased need for surgical intervention, can take 2 weeks to 9 months to take effect
- Refractory hematuria: best managed with surgical outlet procedures
Prostate Cancer
- Usually caused by locally advanced cancer with bladder invasion
- Management: consider ADT, palliative XRT, channel TURP, cystoprostatectomy w/ diversion
Urethrorrhagia
- Trauma: most common non-gender specific cause, maintain catheter for 3-7 days
- Urethritis can be infectious or chemical induced
- Urethral tumors: consider if history urothelial cancer
Upper tract causes
- Presentation: clot colic, anemia, and wormlike clots in urine
- Nephropathies: look for dysmorphic RBCs and casts on UA, systemic symptoms
- Papillary necrosis: sickle cell, NSAID use
- Localized management: may require embolization or partial/total nephrectomy
Random causes of hematuria to rule out
- TB/Schistosomiasis: travel to endemic areas
- ADPKD: family history
- Endometriosis or uterouro fistula: cyclical hematuria during menstrual cycle
- Ureteroiliac fistula: hx vascular surgery, chronic ureteral stents, pelvic XRT
- Arteriovenous malformation: may occur if recent renal procedure, treat w/ embolization
- Nutcracker syndrome: compression of renal vein between aorta and SMA
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Common Causes
- XRT: seen in up to 5% after pelvic XRT
- Chemotherapy: seen in 2-40% after cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, resolves in 60-90% with mesna
- Viral (BK polyoma): more common in children or immunocompromised
Medical Management
| Drug | Mechanism | Dosing | Considerations | Needs OR/Anesthesia? | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Alum Aluminum ammonium sulfate Aluminum potassium sulfate |
Protein precipitation Vasoconstriction |
1% solution (10g/L) run at 200-300mL/hr |
Success: 45-100% No need for anesthesia Can give with VUR |
No | None | Aluminum toxicity |
| Amicar Aminocaproic acid |
Inhibits fibrinolysis | 1g/L intravesical 5g PO loading dose + 1g/hr Give for 24hr after hematuria resolves |
Success: up to 92% | Bladder clots present (causes them to harden) DIC Upper tract bleeding (causes glomerular thrombosis) Risk factors for thrombosis |
Rhabdomyolysis (monitor CPK if used for > 24hr) Hypotension GI effects |
|
| Silver Nitrate | Chemical coagulation | 0.5-1% instilled for 10-20 minutes Rinse out with saline |
Mix with water (will precipitate in saline) | Sometimes (if high concentrations) | Extravasation VUR (need to occlude ureters) Inability to tolerate general/spinal anesthesia |
Bladder scarring Ureteral strictures if VUR |
| Formalin | Cellular protein precipitation | 1-4% solution 300mL or up to bladder capacity hold for 10-15 minutes Irrigate bladder with 1L water/saline |
Success: 80-90% | Yes |
Hyperbaric oxygen
- Technique: 100% O2 at 2-3 atm, 90 minutes, 30-40 sessions
- Benefits: enhances angiogenesis, vasoconstriction, antibiotic efficacy, neutrophil function
- Absolute contraindications: cisplatin/doxorubicin treatment, untreated pneumothorax, active viral infections
- Relative contraindications: seizure risk, poorly controlled DM, emphysema, optic neuritis, glaucoma, current pregnancy, fever, active malignancy, hx sinus/ear surgery, hx spontaneous pneumothorax, spherocytosis, claustrophobia
- Success for XRT cystitis: 80-90% response rate, but 5yr success only 27%
- Side effects: claustrophobia (20%), otalgia (17%), seizures (rare)
Surgical/procedural interventions
| Treatment | Tips |
| Nephrostomy tubes | Avoids bladder exposure to urokinase, allowing clots to form Can be performed with ureteral coiling |
| Internal iliac artery embolization | Can be performed unilaterally/bilaterally Posterior occlusion results in significant gluteal pain Success: up to 90% |
| Cystectomy + Urinary Diversion | Complications in up to 80% if bladder not removed High risk of complications |
References
- AUA Core Curriculum
- Barocas, Daniel A., et al. "Microhematuria: AUA/SUFU Guideline." The Journal of urology 204.4 (2020): 778-786.
- Boorjian, et al. "Evaluation and management of hematuria." Campbell-Walsh Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier (2020): 247-259.
- Castle, E., C. Wolter, and M. Woods. "Evaluation of the Urologic Patient: Testing and Imaging." Campbell-Walsh Urology 12 (2020).
- Lee, Joo Yong, et al. "Hematuria grading scale: a new tool for gross hematuria." Urology 82.2 (2013): 284-289.
- Stout, Thomas E., Michael Borofsky, and Ayman Soubra. "A visual scale for improving communication when describing gross hematuria." Urology 148 (2021): 32-36.
- Wieder JA: Pocket Guide to Urology. Sixth Edition. J.Wieder Medical: Oakland, CA, 2021.